Compare the rate of condensate flow from the pipe in Problem 8.28 (air pressure = 200 kPa) with that for a 3.89-cm-OD pipe and 200 kPa air pressure. What is the rate of condensate flow if the 2 cm pipe is submerged in a 20°C constant-temperature water bath?
GIVEN
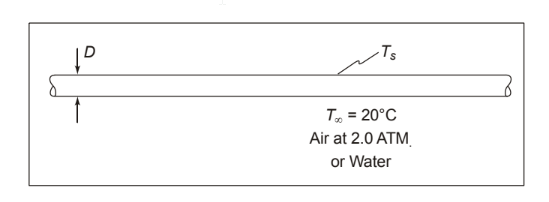
• A long horizontal copper pipe carrying saturated steam within an environmental testing chamber or a water bath
• Steam pressure = 120 kPa
• Ambient pressure (P) = 2 atm
• Ambient air or water temperature (T?) = 20°C
FIND
Rate of condensate flow for
(a) Diameter (D) = 3.89 cm = 0.0389 m Fluid is air at 2.0 atm
(b) Diameter (D) = 2 cm = 0.02 m Fluid is water at T? = 20°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• Pressure change has no effect on absolute viscosity, thermal conductivity, or specific heat of the air
• Air is still
• Convective thermal resistance on the inside of the pipe is negligible
• Thermal resistance of the copper pipe is negligible
• The air behaves as an ideal gas
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
For saturated steam at 0.12 MPa, the heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2238 kJ/kg, and the temperature (Ts) = 105°C.
for dry air at the mean temperature of 62.5°C and one atmosphere
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00298 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0281 W/(m K)
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 at P = 2.0 Atm,
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 9.83 × 10–6 Ns/m2
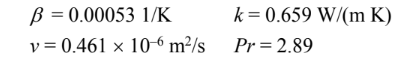
The Grashof number is

Both cases fall within the range of requirements for the use

The condensate flow rate per meter of pipe is given by

COMMENTS
The rate of condensate flow with a 2-cm-diameter pipe in air at 200 kPa. is 2.1 g/min. A change in the fluid from air to water leads to a much larger increase in the rate of condensate flow (100 times) than an increase in the pipe diameter to 3.89 cm (1.6 times).
You might also like to view...
The horizontal axis (X-axis) of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is labeled with _______________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
The orbits of most of the planets in our solar system have eccentricities close to zero
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
When a sample of water at 0.0°C is cooled to –36.0°C and freezes in the process, 935,000 kJ of heat is liberated. What is the mass of this sample of water?
For water LF = 334,000 J/kg, LV = 2.256 × 106 J/kg, and the specific heat of ice is 2050 J/kg ? C°. A) 2290 kg B) 12,700 kg C) 2800 kg D) 1145 kg
When an electrical switch is closed or opened in the vicinity of an operating AM radio, a burst of static can be heard. Which of the following, involving the throwing of the switch, would likely be the cause for this static?
a. The sound from the switching is the source of waves. b. Unnoticed lightning hits nearby every time the switch is thrown. c. Static happens without any cause. d. Electrons are accelerated during the switching process.