When supply is perfectly elastic, the value of the price elasticity of supply is
a. 0.
b. 1.
c. greater than 0 and less than 1.
d. infinity.
d
You might also like to view...
The figure above shows the marginal social cost curve of generating electricity and the marginal private cost curve. The marginal cost paid by the producers and everyone else in society when 100 billion kilowatt hours are produced is
A) 0¢ per kilowatt. B) 5¢ per kilowatt. C) 10¢ per kilowatt. D) 20¢ per kilowatt. E) 15¢ per kilowatt.
Perfectly competitive markets are efficient because
A) they always reach equilibrium. B) firms in the market are price takers. C) the cost to society for producing the goods is exactly equal to the value that society places on the good. D) the long run equilibrium assures that the prices of resources will not increase.
If a nation has the lowest opportunity cost of producing a good, that nation has a(n) ________ in the production of that good.
A. comparative advantage B. comparative advantage and an absolute advantage C. absolute advantage D. absolute advantage and possibly a comparative advantage
In the figure below, we see an expansion of the production-possibility curve (from PPC1 to PPC2). The two goods produced are wheat and cloth, which are land-intensive and labor-intensive, respectively. The outward shift of the production-possibility curve shows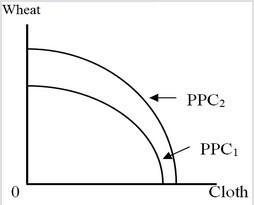
A. biased growth. B. a move from a no-trade situation to free trade. C. an increase in the production costs of both goods. D. balanced growth.