A hoop (I = MR2) is rolling along the ground at 10 m/s. It comes to a hill and starts going up. Assuming no losses to friction, how far does it travel vertically up the hill before it stops?
a. 10 m
c. 5.1 m
b. 3.7 m
d. 7.7 m
A
You might also like to view...
An engineer uses a river 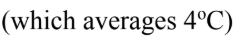 to cool his electrical plant which heats water with a boiler operating at
to cool his electrical plant which heats water with a boiler operating at  What’s the maximal performance (in terms of efficiency) theoretically possible for this electrical plant?
What’s the maximal performance (in terms of efficiency) theoretically possible for this electrical plant?
A. 64% B. 36% C. 27% D. 73%
One _____ equals the distance to an imaginary star that has a parallax of 1 arc second
A) parsec B) light year C) astronomical unit D) kilometer
Graphical Addition: If three vectors add to zero, they must all have equal magnitudes.
A. True B. False
Suppose you live at latitude 40ºN. Which of the following describes the path of the celestial equator through your sky?
A) It extends from due east on your horizon, to an altitude of 50º in the south, to due west on your horizon. B) It extends from due south on your horizon, to your zenith, to due north on your horizon. C) It extends from due east on your horizon, to an altitude of 40º in the south, to due west on your horizon. D) It extends from due east on your horizon, to an altitude of 40º in the north, to due west on your horizon.