Refer to Figure 11-1. If the marginal product of labor curve was plotted on this figure, with marginal product on the vertical axis, the marginal product of labor curve would
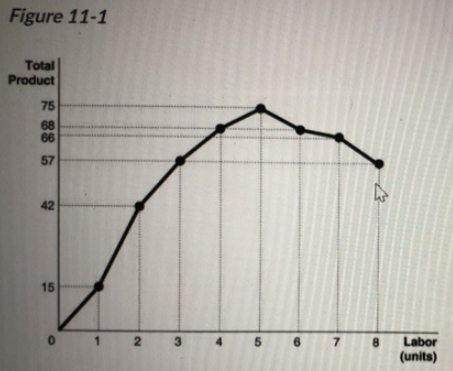
A) never intersect the horizontal axis.
B) intersect the horizontal axis at a point between the 5th and 6th unit of labor.
C) intersect the horizontal axis at a point between the 6th and 7th unit of labor.
D) intersect the horizontal axis at a point somewhere beyond the 8th unit of labor
Answer: B) intersect the horizontal axis at a point between the 5th and 6th unit of labor.
Explanation: The total product declines between the 5th and 6th unit of labor. This means the marginal product is negative and the marginal product curve would intersect the horizontal axis.
You might also like to view...
According to the permanent-income hypothesis, a transitory increase in a person's income will
A) increase consumption more than savings. B) increase savings more than consumption. C) be smoothed out to where the increases in consumption and savings are roughly equal. D) have the same effect on consumption as a permanent increase in income.
Repair guarantees are a sign the seller thinks they have a lemon.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Patents, tariffs, and quotas are all examples of
A) government-imposed barriers. B) economic regulations that increase efficiency. C) entry barriers that improve a country's standard of living. D) entry barriers that protect consumers.
Suppose there was a debate regarding how to spend $1 billion in newly found revenues in the budget. Suppose the centrist Democrat suggests an increase to infrastructure spending. Suppose the centrist Republican suggests an increase in cyber-defense spending. Each is arguing that their plan will get the most good for the money. What is going on here?
A. Both are employing marginal analysis, just from different perspectives. B. Only the Republican is using marginal analysis. C. Only the Democrat is using marginal analysis. D. Neither are using marginal analysis.