Assume that a purely competitive firm uses two resources—labor (L) and capital (C)—to produce a product. In which situation would the firm be maximizing profit?
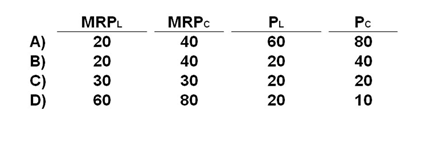
A. Choice A
B. Choice B
C. Choice C
D. Choice D
B. Choice B
You might also like to view...
The potential adult work force includes:
A) non-institutional population 13 years and over plus people on active duty in the military. B) non-institutional population 16 years and over plus people on active duty in the military. C) non-institutional population 18 years and over. D) civilian non-institutional population 16 years and over.
When a U.S. firm sells a good abroad for, say, 100 euros (assume $1.5=1euro), U.S. net exports increase by $150. These $150 in exports can be accounted for as $150 increase in capital outflow because ________
A) private consumption in the foreign country increases by $150 B) if the U.S. firm uses the 100 euros to buy a share of stock in a foreign firm, the firm is supplying U.S. capital to that foreign firm C) if the U.S. firm uses the proceeds to buy a U.S. bond, capital investment in the foreign country has increased D) all of the above E) none of the above
Modern economists are increasingly using microeconomic analysis in macroeconomics because
A) microeconomic theory is more scientific. B) aggregate outcomes stem from decisions made by individuals, business firms and government. C) macroeconomic subjects such as inflation affect all individuals. D) macroeconomics is older and more outdated.
When a game has multiple equilibria, a useful method to sort out which one would be the "best" prediction is to
a. find the one (if any) in which both players are better off than in any other equilibrium. b. find the equilibrium that is symmetric, if any. c. find the one which seems "focal", if any. d. all of the above.