In this experiment an ice bath is used and ice cold isopropyl alcohol. If this procedure is performed and care is not taken to use ice cold alcohol, the yield of DNA decreases. Why do you think it is important to use ice cold alcohol?
A) Cold temperatures slow down enzymes, thus protecting DNA from enzymes that could break it down.
B) Cold temperatures help DNA to precipitate and not become soluble.
C) Both of the choices above help explain why ice cold alcohol should be used.
C) Both of the choices above help explain why ice cold alcohol should be used.
You might also like to view...
Transformation and homologous recombination allow for the formation of heteroduplex DNA. Which of the following would occur during DNA replication of this molecule?
A) One daughter strand is complementary to the recombinant DNA molecule, while the other daughter strand is complementary to the parent DNA molecule. B) Both daughter strands are complementary to the recombinant DNA molecule. C) Both daughter strands are complementary to the parent DNA molecule. D) None of the answers are correct.
Which of these proteins identify a cell as a target cell for a hormone?
a. receptors b. neuromodulators c. cyclic AMP d. response proteins e. neurotransmitters
Which step in this process requires use of restriction enzymes?
A) step A
B) step B
C) step C
D) step D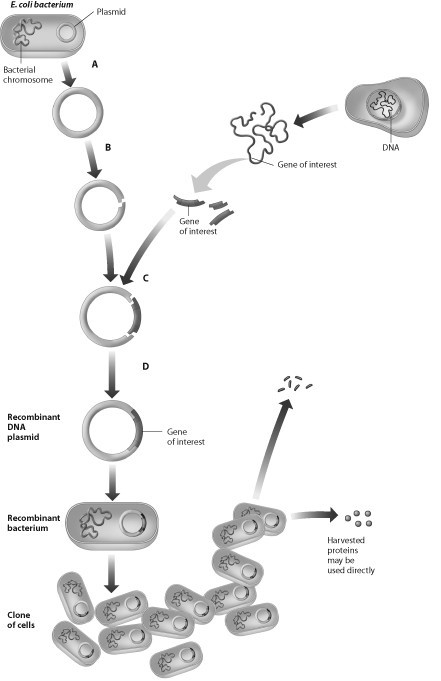
According to the theory of secondary endosymbiosis, __________.
a. cells that had obtained their plastids through endosymbiosis were engulfed and themselves became plastids in heterotrophic eukaryotic cells b. multicellularity evolved when primitive cells incorporated prokaryotic cells that then took on specialized functions c. the symbiotic associations found in coral result from the incorporation of dinoflagellates into coral animal d. the infoldings and specializations of the plasma membrane led to the evolution of the endomembrane system e. mitochondria originated from a heterotrophic prokaryotic endosymbiont