What are the advantages from the 2002 change in the Fed's lending policy?
What will be an ideal response?
Prior to 2002 the Fed set a discount rate that was below the target federal funds rate and then really dissuaded banks from borrowing. A bank had to show it was credit worthy by having collateral for the loans and banks had to exhaust other sources. Often this resulted in driving the market federal funds rate well above the target rate set by the Fed. In 2002 the Fed changed their lending policy to provide loans to any bank in good financial shape and to make these loans at a rate above the market rate, (100 basis points above). Now a bank that has adequate collateral has an incentive to borrow from the Fed if the market rate is more than 100 basis points above the target rate. The fact that financially healthy banks can borrow from the Fed at this higher rate should, most of the time, place an upper limit on how much the market federal funds rate exceeds the target rate, therefore lowering the volatility of the market rate around the target rate.
You might also like to view...
Use the following given market-for-money diagrams to answer the next question.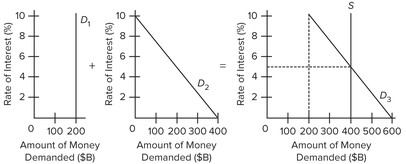 The asset demand for money is shown by
The asset demand for money is shown by
A. D1. B. D2. C. D3. D. S.
The basic human tendency to overvalue recent experience when trying to predict the future is called:
A. tulip mania. B. the leverage effect. C. herd instinct. D. the recency effect.
Because neoclassical economists assume that people are rational decision makers, they:
A. are able to make better predictions about economic behaviors and outcomes. B. ignore the mental processes by which these decisions are made. C. believe that people never make suboptimal decisions. D. believe it is best to limit the number of options people have available.
We would expect which of the following to occur when the central bank pursues expansionary monetary policy?
A) an increase in bond prices and an increase in the interest rate (i) B) a reduction in bond prices and an increase in i C) an increase in bond prices and a reduction in i D) a reduction in bond prices and a reduction in i E) none of the above