Suppose that a pipe carrying a hot fluid with an external temperature of Ti and outer radius ri is to be insulated with an insulation material of thermal conductivity k and outer radius ro. Show that if the convective heat transfer coefficient on the outside of the insulation is h and the environmental temperature is T?, the addition of insulation can actually increases the rate of heat loss if ro < k /h and that maximum heat loss occurs when ro = k/h . This radius, rc, is often called the critical radius.
GIVEN
An insulated pipe External temperature of the pipe = Ti Outer radius of the pipe = ri Outer radius of insulation = ro Thermal conductivity = k Ambient temperature = T? Convective heat transfer coefficient = h
FIND
Show that (a) The insulation can increase the heat loss if ro < k/h (b) Maximum heat loss occurs when ro = k/h
ASSUMPTIONS
The system has reached steady state The thermal conductivity does not vary appreciably with temperature Conduction occurs in the radial direction only
SKETCH
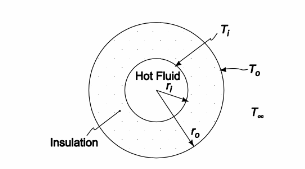
Radial conduction for a cylinder of length L is given
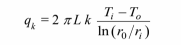
Convection from the outer surface of the cylinder is given
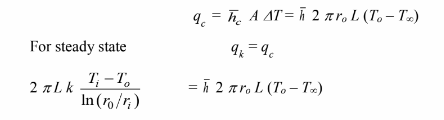
The outer wall temperature, To, is an unknown and must be eliminated from the equation
Solving for Ti – To
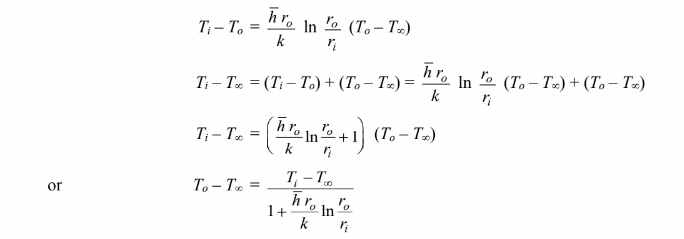
Substituting this into the convection equation
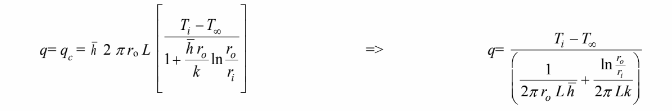
Examining the above equation, the heat transfer rate is a maximum when the term
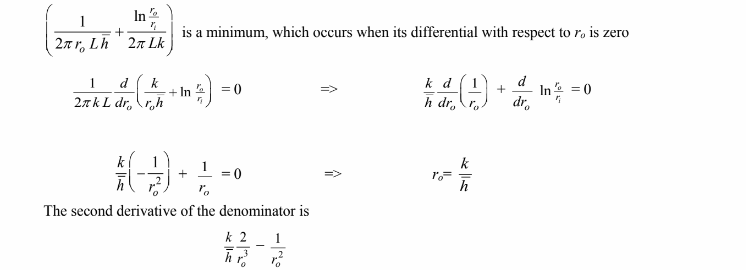
which is greater than zero at ro = k/h, therefore ro = k/h is a true minimum and the maximum heat loss occurs when the diameter is ro = k/h. Adding insulation to a pipe with a radius less than k/h will increase the heat loss until the radius of k/h is reached.
You might also like to view...
The bulk modulus of aluminum is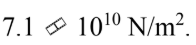 If the density of aluminum is
If the density of aluminum is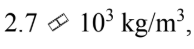 then what is the speed of sound in aluminum?
then what is the speed of sound in aluminum?
A. 4,500 m/s B. 4,700 m/s C. 4,900 m/s D. 5,100 m/s E. 5,500 m/s
A particle (charge = 5.0 ?C) is released from rest at a point x = 10 cm. If a 5.0-?C charge is held fixed at the origin, what is the kinetic energy of the particle after it has moved 90 cm?
A. 1.6 J B. 2.0 J C. 2.4 J D. 1.2 J E. 1.8 J
The diagram represents energy levels in a hydrogen atom. The labeled transitions (A through E) represent an electron moving between energy levels
Suppose that an electron in a hydrogen atom absorbs 10.2 eV of energy, so that it moves from level 1 to level 2. What typically happens next? A) The electron remains in level 2 until it absorbs an additional 10.2 eV of energy. B) The electron jumps to level 3 as soon as it absorbs any additional energy. C) A different electron drops into level 1, since it is now unoccupied. D) The electron returns to level 1 by emitting an ultraviolet photon with 10.2 eV of energy.
Mass is a vector quantity
Indicate whether the statement is true or false