A general condition that two waves undergo destructive interference is
A. their phase difference is zero.
B. their phase difference is
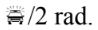
C. their phase difference is
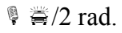
D. their phase difference is an even integral multiple of
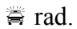
E. their phase difference is an odd integral multiple of
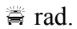
E. their phase difference is an odd integral multiple of
You might also like to view...
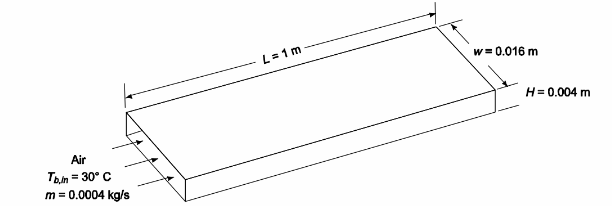
Air at 30°C enters a rectangular duct 1-m-long and 4 mm by 16 mm in cross-section at a rate of 0.0004 kg/s. If a uniform heat flux of 500 W/m2 is imposed on both of the long sides of the duct, calculate (a) the air outlet temperature (b) the average duct surface temperature, and (c) the pressure drop.
GIVEN
• Air flowing through a rectangular duct
• Inlet bulk air temperature (Tb,in) = 30°C
• Duct length (L) = 1 m
• Duct height (H) 4 mm = 0.004 m
• Duct width (w) = 16 mm = 0.016 m
• Air mass flow rate ( m ) = 0.0004 kg/s
• Uniform heat flux (q/A) = 500 W/m2 on the long sides
FIND
(a) Air outlet temperature (Tb,out)
(b) The average duct surface temperature (Ts)
(c) The pressure drop (? p)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The short sides of the duct are insulated
• Entrance effects are negligible
SKETCH
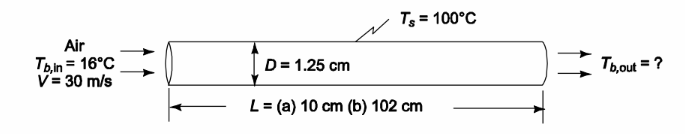
Air at 16°C and atmospheric pressure enters a 1.25-cm-ID tube at 30 m/s. For an average wall temperature of 100°C, determine the discharge temperature of the air and the pressure drop if the pipe is (a) 10-cm-long and (b) 102-cm-long.
GIVEN
• Atmospheric air flowing through a tube
• Entering air temperature (Tb,in) = 16°C
• Tube inside diameter (D) = 1.25 cm = 0.0125 m
• Air velocity (V) = 30 m/s
• Average wall surface temperature (Ts) = 100°C
FIND
The discharge temperature (Tb,out) and the pressure drop (?p) if the pipe length (L) is
(a) 10 cm (0.1 m) (b) 102 cm (1.02 m)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• The tube is smooth
SKETCH
for dry air at the entering bulk temperature of 16°C
Density (?) = 1.182 kg/m3
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0248 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 15.3 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
Specific heat (c) = 1012 J/(kg K)
The movement of a pool ball, after being struck by a cue, is an example of
A) Newton's first law of motion. B) Newton's second law of motion. C) Newton's third law of motion. D) the universal law of gravitation. E) conservation of momentum.
Natural objects of the solar system that strike earth are called
A) comets B) meteors C) asteroids D) meteorites