What is (are) the location(s) of the low tide(s) on Earth caused by the gravitation of the Moon? Give the location(s) relative to the line through the Earth's and Moon's centers, line EM
a. the point on EM on the Earth's surface nearest to the Moon
b. the point on EM on the Earth's surface farthest from the Moon
c. the points on the Earth's surface perpendicular to EM at the Earth's center
d. the points on EM on the Earth's surface nearest to and farthest from the Moon
C
You might also like to view...
Two identical tiny balls of highly compressed matter are 1.50 m apart. When released in an orbiting space station, they accelerate toward each other at 2.00 cm/s2. What is the mass of each of them? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ? m2/kg2)
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is true about frictional forces?
a. They are stored as frictional potential energy. b. They can decrease kinetic energy. c. They can increase kinetic energy. d. They produce heat potential energy. e. They eventually convert to electromagnetic potential energy.
Any main-sequence star over 25 solar masses will probably retain enough matter in its core after its supernova to make a black hole
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
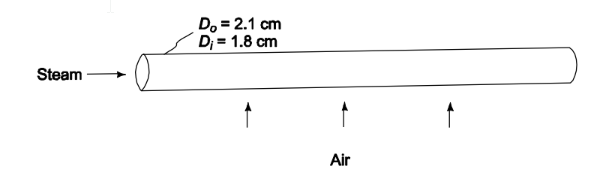
In a heat exchanger, as shown in accompanying figure, air flows over brass tubes of 1.8- cm-ID and 2.1-cm-OD that contain steam. The convection heat-transfer coefficients on the air and steam sides of the tubes are 70 W/(m2 K) and 210 W/(m2 K), respectively. Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger (a) based on the inner tube area, (b) based on the outer tube area.
GIVEN
• Air flow over brass tubes containing steam
• Tube diameters
? Inside (Di) = 1.8 cm = 0.018 m
? Outside (Do) = 2.1 cm = 0.021 m
• Convective heat transfer coefficients
? Air side h c= 70 W/(m2 K)
? Steam side h i= 210 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger based on
(a) the inner tube area (Ui) and
(b) the outer tube area (Uo)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The heat transfer coefficients are uniform over the transfer surfaces
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the thermal conductivity of brass at 20°C (kb) = 111 W/(m K)