Identify and explain the three ways we can use macroeconomic analysis.
What will be an ideal response?
Macroeconomics explains why some resources increase over time and how an increase in these resources translates into a higher standard of living. In the fastest-growing countries, citizens save a large fraction of the money they earn. Firms can then borrow the funds saved to purchase machinery and equipment that make their workers more productive. The fastest growing countries also have well-educated workforces, allowing firms to quickly adopt new technologies that increase worker productivity. All economies, including ones that experience a general trend of growth, are subject to economic fluctuations including periods when the economy shrinks. During an economic downturn, some of the economy's resources are idle. Many workers are unemployed, and many factories and stores are closed. By contrast, sometimes the economy grows too rapidly, causing inflation. Macroeconomics helps us understand why these fluctuations occur, why the economy sometimes cools and sometimes overheats and what we can do to moderate the fluctuations. A third reason for studying macroeconomics is to make informed business decisions. A manager who intends to borrow money for a new factory or store could use her knowledge of macroeconomics to predict the effects of current public policies on interest rates and then decide whether to borrow the money now or later.
You might also like to view...
The economist in the 1930s who is credited with key insights into causes of economic downturns was:
A. John Maynard Keynes B. Ben Bernanke C. Adam Smith D. David Ricardo
Refer to Figure 10.2. Which line represents wealth?
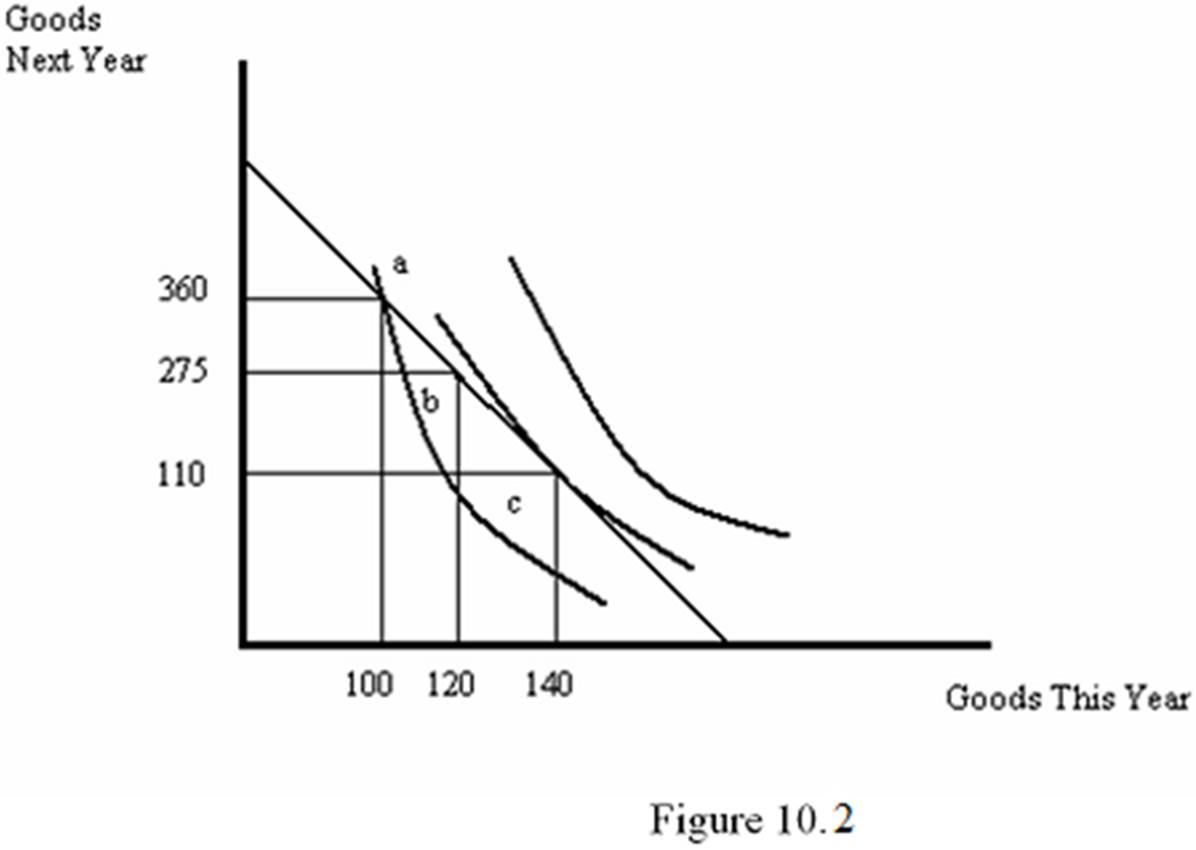
A. b
B. h
C. f + i
D. g
During which of the following periods was the price level most unstable?
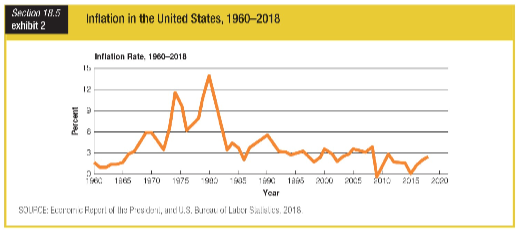
a. 1960–1965
b. 1970–1975
c. 1990–1995
d. 2000–2005
A monopoly firm selling textbooks to students in a small town is currently maximizing profits by charging a price of $50 per book. It follows that the marginal cost of textbooks is:
A. less than $50. B. equal to $50. C. greater than $50. D. greater than the average total cost.