Negative externalities lead markets to produce
a. greater than efficient output levels and positive externalities lead markets to produce smaller than efficient output levels.
b. smaller than efficient output levels and positive externalities lead markets to produce greater than efficient output levels.
c. greater than efficient output levels and positive externalities lead markets to produce efficient output levels.
d. efficient output levels and positive externalities lead markets to produce greater than efficient output levels.
a
You might also like to view...
Income in kind is defined as
A) income received in the form of a paycheck. B) payment for services in the form of cash. C) tips. D) income received in the form of goods and services.
In the circular-flow diagram, the two types of markets in which households and firms interact are the markets for goods and services and the markets for factors of production
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Figure 4-25
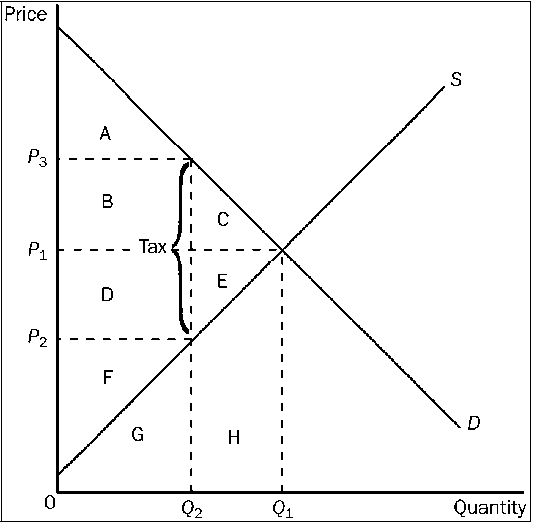
Refer to . The benefit to the government is
a.
measured by tax revenue and is represented by area A + B.
b.
measured by tax revenue and is represented by area B + D.
c.
measured by the net gain in total surplus and is represented by area B + D.
d.
measured by the net gain in total surplus and is represented by area D + E.
Which of the following Gauss-Markov assumptions is violated by the linear probability model?
A. The assumption of constant variance of the error term. B. The assumption of zero conditional mean of the error term. C. The assumption of no exact linear relationship among independent variables. D. The assumption that none of the independent variables are constants.