What is the argument against the use of autonomous tightening of monetary policy in response to a credit-driven asset-price bubble?
What will be an ideal response?
Though a bubble may have begun with an abundance of credit seeking a profitable use, restricting credit is unlikely to dampen enthusiasm for assets that are "known" to be profitable. Indeed, a tightening of credit may impact only those who do not yet possess the lucrative bubble assets and enhance the rewards for those who do. Thus, the credit tightening ensures that the "patient" (the economy) is thoroughly weakened before the "medicine" of financial discipline takes effect.
You might also like to view...
A firm's opportunity costs ________
A) equal the costs of resources it buys from others in the market B) include the cost of using resources owned by the firm C) increase when economies of scope exist D) do not include any opportunity costs for resources the owner suppliers
Assume that the expectation of a recession next year causes business investments and household consumption to fall, as well as the financing to support it. If the nation has low mobility international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real GDP and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? a. Real GDP falls
and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more negative (or less positive). b. Real GDP rises and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more negative (or less positive). c. Real GDP falls and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more positive (or less negative). d. Real GDP falls and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance falls. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
Figure 17-10
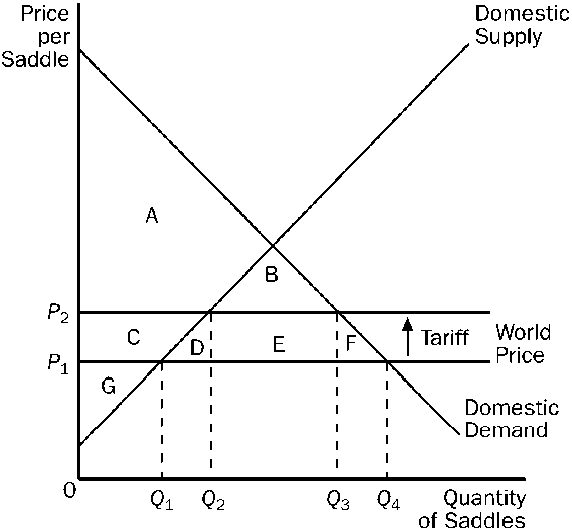
Refer to . With the tariff, the domestic price and domestic quantity demanded are
a.
P1 and Q1.
b.
P1 and Q4.
c.
P2 and Q2.
d.
P2 and Q3.
The network effect in the TV broadcasting industry results in
A) a positive market feedback between the number of advertisers and the size of TV audience. B) a negative market feedback between the number of advertisers and the size of TV audience. C) a positive market feedback between the number of advertisers and the number of TV channels. D) a negative market feedback between the number of advertisers and the number of TV channels.