The trade-off between current consumption and the production of capital goods is also a trade-off between
A) the future cost for capital goods and future cost of consumption goods.
B) having fewer needs and more wants in the future.
C) satisfying the needs of the poor and the wants of the wealthy.
D) current consumption and future consumption.
D
You might also like to view...
Economists are interested in long-term economic growth because growth increases real GDP per person and improves our standard of living
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Marginal profit is the profit
A. earned by a firm that is about to go out of business. B. calculated directly from the total cost curve. C. that is added by a one-unit increase in total output. D. earned for each dollar of cost increase.
Firms in industrial countries find a larger market for their goods in other industrial countries than in developing countries because:
a. the consumption patterns in the industrial countries are highly heterogeneous. b. the trade policies of the industrial nations are more favorable than the developing countries. c. the industrial countries tend to have a higher population than the developing countries. d. the industrial countries are capital intensive countries. e. the consumption patterns in the industrial countries are more or less uniform.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.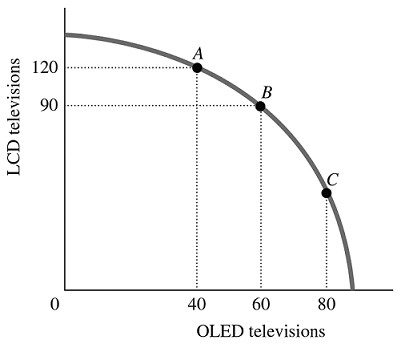 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point B. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point A is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point B. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point A is the
A. 120 LCD TVs that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED TVs. B. 30 LCD TVs that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED TVs. C. 20 OLED TVs that must be forgone to produce 30 additional LCD TVs. D. 40 OLED TVs that must be forgone to produce 120 additional LCD TVs.