A monopolist faces a demand curve that
A) is perfectly horizontal at the market price.
B) is below the marginal revenue curve.
C) is downward sloping.
D) coincides with the industry supply.
C
You might also like to view...
The effect of a government subsidy in a market where a positive externality is present is:
A. to increase surplus. B. to increase efficiency. C. to make consumers internalize the external benefit. D. All of these statements are true.
Suppose the accompanying figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve and marginal cost curve for a monopolist.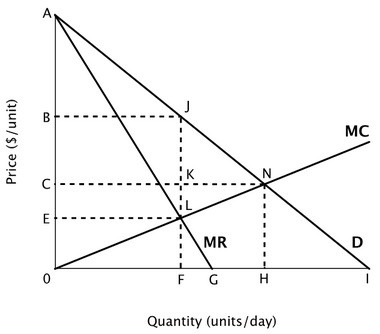 The socially optimal level of output is ________ units per day.
The socially optimal level of output is ________ units per day.
A. I B. F C. G D. H
Suppose that David buys the same number of energy drinks every weekend no matter what happens to the price of the energy drinks. What does this suggest about David's demand for energy drinks?
A. It is elastic. B. It is perfectly inelastic. C. It is unit elastic. D. It is not something that can be characterized without knowing the prices of the energy drinks.
The benefits of social regulation are
A) easy to measure by the marginal value method. B) often difficult to measure. C) obvious to almost everyone, but the costs are usually hidden. D) greater than the costs of social regulation in every example in the country today.