What are the means for the main effect of the Apology variable? [Be sure to specify which mean belongs with each condition.]
A researcher examined whether people's responses to injustice depend on whether the offender in a hypothetical scenario is a male or a female, and whether the offender apologized (or not) after the offense. Participants were randomly assigned to the gender of the offender condition (female, male) and apology condition (present, absent).
Participants read a hypothetical scenario in which a person (male or female) acted unjustly and the action results in severe harm. Half of the participants read that the offender apologized; the other half read the same scenario except no apology was mentioned. Participants then rated the extent to which they would forgive the offender using a 0 (no forgiveness) to 9 (complete forgiveness) rating scale. The researcher predicted that participants' forgiveness would be greater following an apology compared to the apology-absent condition. The researcher also predicted that the gender of the offender would have no effect on forgiveness.
The researcher observed the following means:
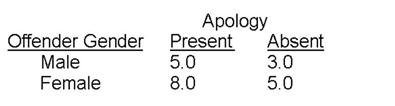
The mean forgiveness rating for the Apology-Present condition is 6.5; the mean rating for the Apology-Absent condition is 4.0.
You might also like to view...
A type of dissociative disorder characterized by sudden loss of memory for important personal information that sometimes occurs after a person has endured a traumatic event is a. dissociative amnesia. b. dissociative stress disorder
c. dissociative identity disorder. d. dissociative depressive disorder.
The data from Jerome Kagan’s research program into temperamental differences among young children . . .
a. Is based on extensive parental interviews b. Comes from careful observations of children around the world c. Is based on how children act in a laboratory setting d. Has been transformed into modern statistics from the initial observations of Galen
An almost unlimited amount of information can be stored in:
a. sensory memory c. short-term memory b. long-term memory d. echoic memory
Children find it easier to remember events that follow a _________ and ___________ order than events that do not
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word