The sliding filament model for muscle contraction can be studied using an isolated skeletal muscle that is fixed at each end, while a machine records the tension that is generated when the muscle is stimulated to contract. In one particular muscle tested, the length of the thick filaments was 1.6 ?m, and the length of the thin filaments that project in from each Z line toward the center of the sarcomere was 1.0 ?m. A summary of the results comparing sarcomere length to the degree of tension produced during contraction is shown below. What most likely explains the difference between segment II and segment III of the graph?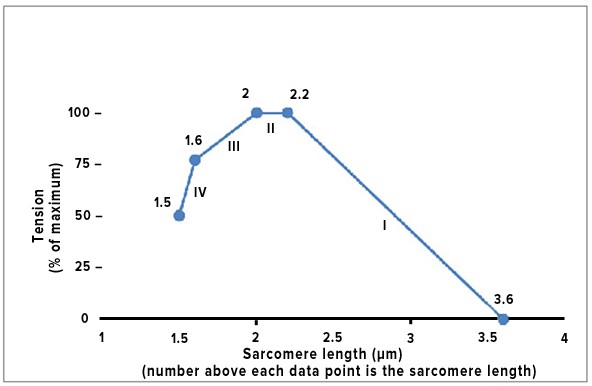
A. There is an increasing overlap of the free ends of the thin filaments in segment III but not in segment II.
B. The distance between the Z lines is constant in segment II but rapidly increasing in segment III.
C. Fewer myosin cross-bridges are forming in segment II than in segment III.
D. The muscle cells used up all the ATP by the end of segment II.
E. The length of the thin filaments is decreasing in segment III but not in segment II.
F. The length of the thick filaments is decreasing in segment III but not in segment II.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
When you are upright, what is the primary mechanism that propels blood in your feet back to your inferior vena cava?
A. recoil of elastic fibers in the walls of the leg veins B. contraction of the left ventricle of the heart C. contraction of smooth muscle in the walls of the leg veins D. contraction of skeletal muscles in your legs E. the valves in the leg veins alternating between open and closed
The regulatory systems of the animal body maintain a relatively stable internal condition through a process called ________.
A. countercurrent exchange B. equilibrium C. homeostasis D. osmoreception E. absorption
In which of the following ways are archaea similar to eukaryotic cells?
a. size
b. shape
c. presence of histones
d. DNA polymerases
e. presence of operons
The size of a metabolizing cell is limited by its
A. surface area-to-volume ratio. B. nuclear size. C. function. D. extracellular matrix. E. genome size.