Crowding out results in a decrease in
A) transfer payments.
B) defense spending.
C) private spending.
D) government spending.
C
You might also like to view...
A tax multiplier equal to ?4.30 would imply that a $100 tax increase would lead to a:
A. $430 decline in real GDP. B. $430 increase in real GDP. C. 4.3 percent increase in real GDP. D. 4.3 percent decrease in real GDP.
Using real GDP on the horizontal axis instead of real disposable income implies that a marginal propensity to consume 0.6 generates for every additional $100 of real GDP, there is
A. $40 of additional saving and taxes. B. $40 of additional consumption spending. C. $4 of additional saving. D. $60 of additional real disposable income.
Any change in the economy that raises desired national saving for a given value of the real interest rate will shift the desired national saving curve to
A. the right and decrease the real interest rate. B. the left and decrease the real interest rate. C. the left and increase the real interest rate. D. the right and increase the real interest rate.
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given D m and S m , an interest rate of i 3 is not sustainable because the:
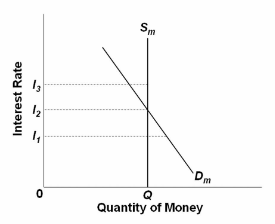
A. supply of bonds in the bond market will decline and the interest rate will rise.
B. supply of bonds in the bond market will increase and the interest rate will decline.
C. demand for bonds in the bond market will decline and the interest rate will rise.
D. demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall.