In a compound microscope
A) both the objective and the eyepiece form real images.
B) magnification is provided by the objective lens and not by the eyepiece. The eyepiece merely increases the resolution of the image viewed.
C) magnification is provided by the objective and not by the eyepiece. The eyepiece merely increases the brightness of the image viewed.
D) the magnification is m1 + M2, where m1 is the lateral magnification of the objective and M2 is the angular magnification of the eyepiece.
E) the image of the objective serves as the object for the eyepiece.
E
You might also like to view...
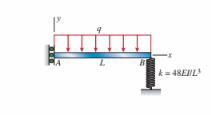
A steel beam (E 5 210 GPa) with I 5 119 3 106 mm4 and span length L 5 3.5 m is subjected to uniform load q 5 9.5 kN/m. The maximum deflection of the beam is approximately:
(A) 10 mm
(B) 13 mm
(C) 17 mm
(D) 19 mm
If F = 4.0 N and m = 2.0 kg, what is the magnitude a of the acceleration for the block shown below? The surface is frictionless.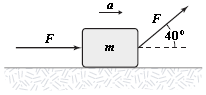
A. 5.3 m/s2 B. 4.4 m/s2 C. 3.5 m/s2 D. 6.2 m/s2 E. 8.4 m/s2
Clevage and fracture are related because
What will be an ideal response?
A proton, with mass 1.67 × 10-27 kg and charge +1.6 × 10-19 C, is sent with velocity 7.1 × 104 m/s in the +x direction into a region where there is a uniform electric field of magnitude 730 V/m in the +y direction
What are the magnitude and direction of the uniform magnetic field in the region, if the proton is to pass through undeflected? Assume that the magnetic field has no x-component and neglect gravitational effects.