Multiplier effects occur when there is a change in spending which does not depend on income. Spending which does not depend on income is referred to as
A) coincident spending.
B) nominal spending.
C) autonomous expenditures.
D) induced expenditures.
C
You might also like to view...
What economic variables would you need to consider in order to distinguish between a developing country with a short-term balance of payments problem and one in a debt crisis? Explain what data you would need to look at and why
What will be an ideal response?
Using Figure 3 below, suppose that the economy was at Y1. This level of GDP would be considered:
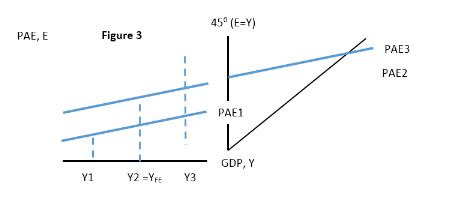
A. inflationary.
B. recessionary.
C. a long run level of output.
D. a natural rate of output.
In the long run, an increase in the price level: a. increases output prices relative to input prices. b. increases the profit margins of many producers. c. increases RGDP supplied
d. Does none of the above.
For economic efficiency, which of the following conditions should be met?
a. Scarcer goods should have lower prices. b. More abundant goods should have lower prices. c. More abundant goods should have higher prices. d. All goods should have equal prices.