During the period 2001-2004, the U.S. Federal Reserve lowered nominal interest rates on the dollar by more than the European Central Bank (ECB) did on the euro, a move that most market participants viewed as temporary. What was the effect on the dollar-euro exchange rate?
a. The dollar depreciated against the euro.
b. The dollar appreciated against the euro.
c. There was no change in the dollar-euro rate because expectations adjusted.
d. There was no change in the dollar-euro rate because real interest rates were unchanged.
Answer: a. The dollar depreciated against the euro
You might also like to view...
Trend refers to
A) increases but not decreases of a variable. B) the difference between the maximum value of the variable and the minimum value of the variable. C) a general tendency for a variable to rise or fall. D) the scale used on the x- and y-axes. E) decreases but not increases of a variable.
In the Malthusian model, improvements in health care lead to
A) higher population and higher per-capita production. B) higher population and lower per-capita production. C) lower population and higher per-capita production. D) lower population and lower per-capita production.
The graph shown best represents:
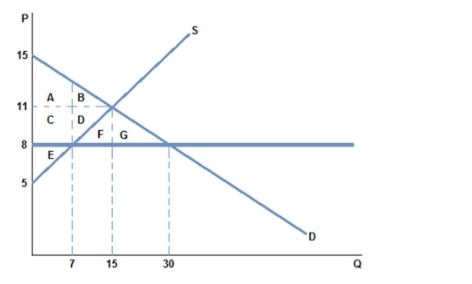
A. a binding price ceiling.
B. a binding price floor.
C. a missing market.
D. a market for an inferior good.
Which of the following is an example of a government program that provides in-kind assistance to the poor?
a. Supplemental Security Income (SSI) b. Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) c. food stamps d. Social Security payments e. unemployment benefits