Suppose a government tried to mandate a real wage above the equilibrium real wage. Assuming that factor markets are otherwise free and competitive, explain why the higher real wage would fail to increase the share of labor income in national income
What will be an ideal response?
Given the Cobb-Douglas production function, the marginal product of labor is , and the marginal product of capital is . If each factor's price is equal to its marginal product, then its share of total income equals its exponent in the production function; 0.7 for labor, and 0.3 for capital. Firms will respond to the mandated higher real wage by reducing the quantity of labor demanded until the marginal product of labor is equal to the real wage. Workers who still have a job will have higher income, but many workers now have no job and no income. The reduced labor input lowers the marginal product of capital. Since the rental price of capital is unregulated, it will fall, so that no capital becomes idle. Since the prices of both labor and capital are equal to their respective marginal products, their shares of the reduced total output are unchanged.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 17-3. What is Hotspur's profit maximizing quantity of labor?
A) 2 workers B) 3 workers C) 5 workers D) 6 workers
Suppose Dean and Kennedy are playing a single stage game. Each simultaneously chooses either 1 or 2. If they both select 1, Dean pays Kennedy $2. If they both pick 2, Dean pays Kennedy $4. If they select different numbers, Kennedy pays Dean $3. Draw a table showing the two players' strategies and payoffs. Are any strategies dominant? Weakly dominant? Dominated? Solve for a mixed strategy equilibrium.
The payoff matrix should appear as follows:
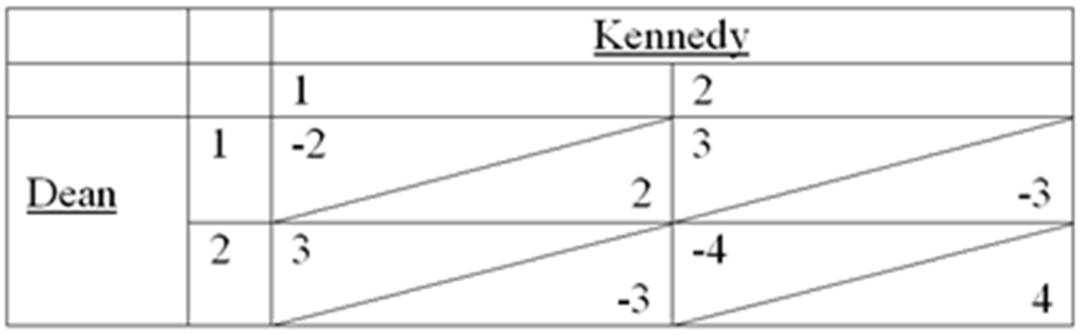
What will be an ideal response?
The irregular and largely unpredictable fluctuations in economic activity are called
a. market failure. b. business cycle. c. inflation. d. unemployment.
Which of the following is correct?
a. Risk-averse people will not hold stock. b. Diversification cannot reduce firm-specific risk. c. The larger the percentage of stock in a portfolio, the greater the risk, but the greater the average return. d. Stock prices are determined by fundamental analysis rather than by supply and demand.