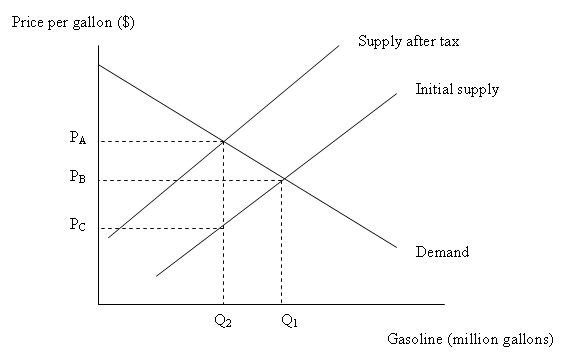
 Figure 16.5Figure 16.5 depicts the market effects of a gasoline tax. What is the amount of gasoline tax per gallon?
Figure 16.5Figure 16.5 depicts the market effects of a gasoline tax. What is the amount of gasoline tax per gallon?
A. PA - PB
B. PB - PC
C. PA - PC
D. There is not sufficient information.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Suppose after the semester ends, you take a trip to a tropical island. Upon arriving at the island, you make a stop at one of the markets and notice that everyone is carrying around jars full of little turtles
You also notice the person in line in front of you just paid for a bottle of rum with 6 turtles. Someone else just bought a straw hat for two turtles. Thinking back to your economics class (as painful as that may be), you would conclude that A) turtle soup is a delicacy. B) turtles are valueless. C) this is a barter economy. D) those little turtles are serving as money.
The table above gives the utility from pens and pencils. The marginal utility derived from the third pen is
A) 200. B) 155. C) 445. D) 45.
Which of the following is a problem with the price system that can lead to fluctuations in output?
A. The price system works silently in the background. B. Prices can be slow to adjust. C. Prices may be flexible. D. All of these
Refer to Scenario 1.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.SCENARIO 1.1: An economist wants to understand the relationship between minimum wages and the level of teenage unemployment. The economist collects data on the values of the minimum wage and the levels of teenage unemployment over time. The economist concludes that a 1% increase in minimum wage causes a 0.2% increase in teenage unemployment. From this information he concludes that the minimum wage is harmful to teenagers and should be reduced or eliminated to increase employment among teenagers.Refer to Scenario 1.1. A graph of the value of the minimum wage on one axis and the level of teenage unemployment on the other axis is an example of
A. an economic theory. B. inductive reasoning. C. an economic model. D. a variable theory.