What is the opportunity cost of going from point E to point D?
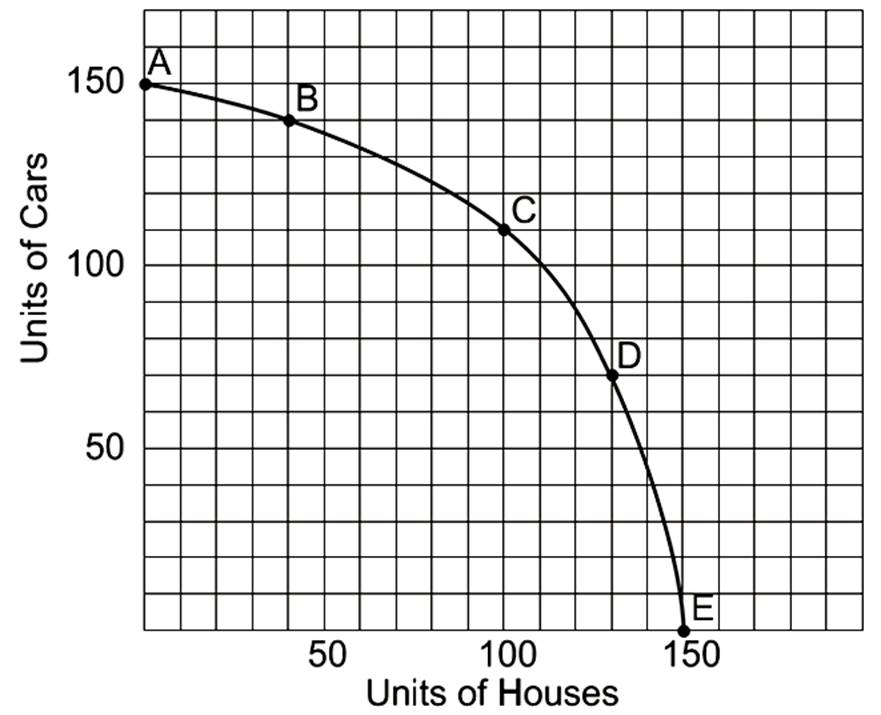
20 houses
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 15-5. In the figure above, the movement from point A to point B in the money market would be caused by
A) a decrease in real GDP. B) an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve. C) an increase in the required reserve ratio by the Federal Reserve. D) an increase in the price level.
The existence of externalities in a market implies that:
a. resources are being used efficiently. b. there is no other allocation of resources that would make society as a whole better off. c. consumers cannot be excluded from consuming the good once it is provided. d. resources are not being used in their highest valued activity. e. the social welfare is maximized.
The market mechanism:
A. Works through central planning by the government. B. Eliminates market failures created by the government. C. Uses prices as a means of communication between consumers and producers. D. Is very inefficient since consumers cannot communicate directly with producers.
There are 10 families in a neighborhood that are affected by noise pollution from a local factory. The noise could be reduced if the company spent $5,000 on technological improvements. The company agrees to make these improvements if the affected families contribute the $5,000. Since there are no legal restrictions governing the factory's noise, the negotiations fail. This outcome is an example of the
A. free-rider problem. B. drop-in-the-bucket problem. C. problem that arises when property rights are not defined. D. Coase theorem.