Briefly explain how reductions in government purchases and tax decreases would influence aggregate demand through the multiplier effect. Give an example.
What will be an ideal response?
Student examples will vary. A sample answer follows: Reductions in government purchases and tax increases are magnified by the multiplier effect. Suppose the government made cutbacks in highway building. Not only would it decrease government purchases directly, but construction workers would be laid off and unemployed workers would cut back on their consumption spending; this initial cutback would have a multiplying effect through the economy, leading to an even greater reduction in aggregate demand. Similarly, tax hikes would leave consumers with less disposable income, so they would cut back on their consumption, which would lower aggregate demand and set off the multiplier process, leading to an even larger cumulative effect on aggregate demand.
You might also like to view...
Assume a competitive price-searcher firm is earning an economic profit. The marginal revenue from selling an additional unit is $30 and the marginal cost of producing that additional unit is $23 . The firm should
a. change neither its price nor its output level b. reduce its price and increase its output level c. increase its price and reduce its output level d. reduce both its price and its output level e. increase both its price and its output level
According to the textbook, the evidence indicates that NAFTA has:
A. reduced the employment of unskilled workers in the United States significantly. B. reduced the wages of skilled workers in the United States. C. stopped illegal immigration from Mexico. D. not significantly reduced the employment of unskilled workers in the United States.
Stagflation refers to a situation in which the economy is experiencing:
A. high economic growth and high inflation. B. low economic growth and high inflation. C. high economic growth and low inflation. D. low economic growth and low inflation.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow.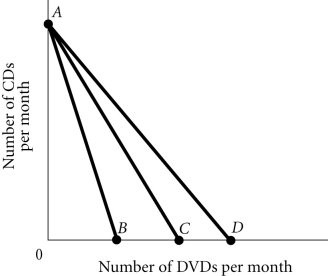 Figure 6.3Refer to Figure 6.3. Molly's budget constraint is AC. Molly can purchase
Figure 6.3Refer to Figure 6.3. Molly's budget constraint is AC. Molly can purchase
A. all of the points along BD. B. none of the points along AD. C. all of the points along AB. D. none of the points along AC.