Gary, Kevin, and Joshua are three individuals who were previously employed but do not have jobs now. Gary lost his job a year ago
Although he would like to have a job, he has given up looking for one as he thinks there are no suitable jobs available for him. Kevin was working as a finance teacher, but quit his job a few months back to become a stock broker. Ever since he quit his job, he is unable to get a new one, although he is actively seeking. Joshua was employed in a steel mill. He lost his job when the labor union in his mill demanded a hike in wages. Classify the three individuals according to their type of unemployment.
Since Gary previously had a job but has stopped looking for one now, he can be considered a discouraged worker. Discouraged workers are potential workers who have stopped looking for jobs since they think there are none available for them.
Kevin is unemployed because it is taking time for him to find a suitable job. Hence, Kevin can be said to be frictionally unemployed. Such unemployment arises because workers have imperfect information about available jobs and need to engage in a time-consuming process of job search.
Joshua is unemployed because the labor union in his workplace demanded higher wages. When wages are above the market clearing wage, there is a fundamental mismatch between the quantity demanded and quantity supplied of labor. Unemployment caused because of this mismatch is referred to as structural unemployment.
You might also like to view...
A market maker faces the following demand and supply for widgets. Eleven buyers are willing to buy at the following prices: $15, $14, $13, $12, $11, $10, $9, $8, $7, $6, $5 . Eleven sellers are also willing to sell at the same prices. If the market maker wants to make three transactions, what should he ask (the buyers)
a. $12 b. $13 c. $14 d. $15
Assume Bryce's budget constraint is represented by line C in the graph shown. Which of the following would cause Bryce's budget constraint to shift to A?
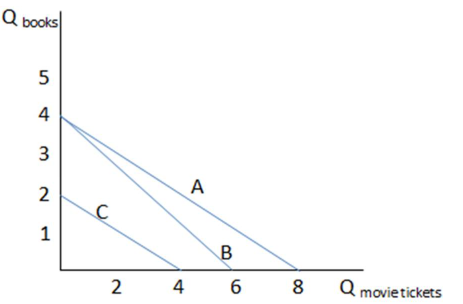
A. Bryce's income increased.
B. Bryce's income decreased.
C. Bryce's preferences for books and movies decreased.
D. Bryce's preferences for books and movies increased.
The law of diminishing marginal utility explains why the demand curve is downward sloping. The law states that as you consume more of a good, the
a. total satisfaction you obtain from consuming the good falls b. added satisfaction you obtain from consuming an additional unit of the good increases at a diminishing rate c. marginal product increases at a diminishing rate d. satisfaction you obtain from each additional unit of the good you consume falls e. total satisfaction you obtain from each additional good you consume decreases at a diminishing rate
Exhibit 8-2 Consumption function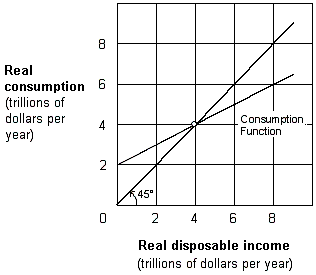
A. at 0 disposable income. B. between $0 and $4 trillion disposable income. C. at $4 trillion disposable income. D. at a disposable income greater than $4 trillion.