Describe the range of sizes and masses of black holes
What will be an ideal response?
The smallest, a three solar mass black hole, is only about 9 km across, but some in the cores of galaxies may be millions of solar masses and larger than the solar system.
You might also like to view...
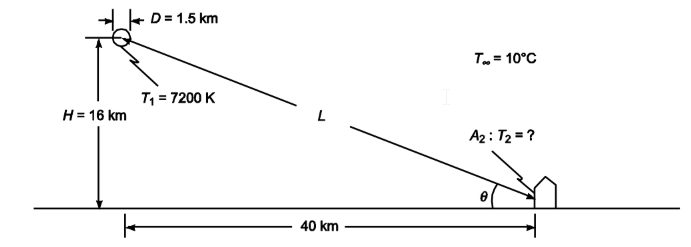
A hydrogen bomb may be approximated by a fireball at a temperature of 7200 K according to a report published in 1950 by the Atomic Energy Commission. (a) Calculate the total rate of radiant-energy emission in watts, assuming that the gas radiates as a blackbody and has a diameter of 1.5 km, (b) If the surrounding atmosphere absorbs radiation below 0.3 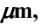 determine the per cent of the total radiation emitted by the bomb that is absorbed by the atmosphere, (c) Calculate the rate of irradiation on a 1 m2 area of the wall of a house 40 km from the center of the blast if the blast occurs at an altitude of 16 km and the wall faces in the direction of the blast, (d) Estimate the total amount of radiation absorbed
determine the per cent of the total radiation emitted by the bomb that is absorbed by the atmosphere, (c) Calculate the rate of irradiation on a 1 m2 area of the wall of a house 40 km from the center of the blast if the blast occurs at an altitude of 16 km and the wall faces in the direction of the blast, (d) Estimate the total amount of radiation absorbed
assuming that the blast lasts approximately 10 sec and that the wall is covered by a coat of red paint, (e) If the wall were made of oak whose flammability limit is estimated to be 650 K and that had a thickness of 1 cm, determine whether or not the wood would catch on fire. Justify your answer by an engineering analysis stating carefully all assumptions.
GIVEN
- A hydrogen bomb fireball
- Fireball temperature (T1) = 7200 K
- Surrounding atmosphere absorbs radiation below 0.3

- The blast occurs at an altitude (H) of 16 km = 16,000 m
FIND
(a) The total rate of radiant-energy emission in watts (qr)
(b) The per cent of the total radiation absorbed by te atmosphere
(c) The rate of irradiation on a 1 m2 area of the wall of a house 40 km (40,000 m) from the center of the blast and facing the blast (G2)
(d) Total amount of radiation absorbed if the blast lasts 10 seconds and the wall is covered with red paint
(e) If the walls are oak with a flammability limit of 650 K and a thickness (s) of 1 cm, will the wood catch fire?
ASSUMPTIONS
- The gas radiates as a blackbody
- Diameter of the fireball (D) = 1.5 km
- The air and surrounding temperature (T?) = 10°C
- The surroundings behave as a blackbody enclosure
- The heat transfer from the oak walls to its surroundings during the 10 seconds of irradiation can be neglected
- The house wall is initially at the surroundings temperature
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant
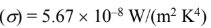
the emissivity of red paint at short wavelengths
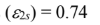
the emissivity of red paint at long wavelengths
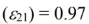
Specific heat
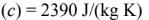
Thermal conductivity
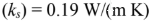
Density
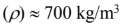
Thermal diffusivity
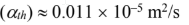
A rock of weight 17.5 N is immersed in a beaker of water while suspended from a spring scale with a reading of 9.00 N. The weight of the beaker and water together is 23.5 N. What is the net force of the beaker on the table?
A. 17.5 N B. 23.5 N C. 32.0 N D. 41.0 N
Which of the following statements regarding the H-R diagrams of star clusters is NOT correct?
A. A very young cluster will have stars that lie in the right-hand side and a little above the main sequence. B. A very young cluster will not show a turn-off point. C. A very old cluster will have many stars in the upper left corner of the H-R diagram. D. A very old cluster will show a turn-off point and will have many red and yellow giant stars. E. A very young cluster will not have all its stars on the main sequence.
Evidence gathered from observations of exoplanets indicates approximately what percentage of stars have planets?
A) 0 B) 1 C) 10 D) 100 E) It is not yet possible to make an estimate.