Explain how the pH of seawater remains slightly alkaline AND relatively constant
What will be an ideal response?
The salinity of seawater is maintained by the carbonate buffering system. When carbon dioxide dissolves in water, a hydrogen ion (H+) and a bicarbonate ion (HCO3?) are formed. The bicarbonate ion (HCO3?) can oxidize and lose an additional hydrogen ion (H+) and form carbonate (CO3?2). The ability of carbonate (CO3?2 ) to gain a hydrogen ion (H+) allows the ocean to maintain a relatively constant pH. When the pH of seawater drops becoming weakly acidic, the carbonate ions (CO3?2 ) combine with hydrogen ions to form bicarbonate, raising the pH. When the pH becomes too alkaline, the bicarbonate ions (HCO3?) in seawater lose hydrogen ions (H+) lowering the pH.
You might also like to view...
During a La Niña phase, excess warm water accumulates in
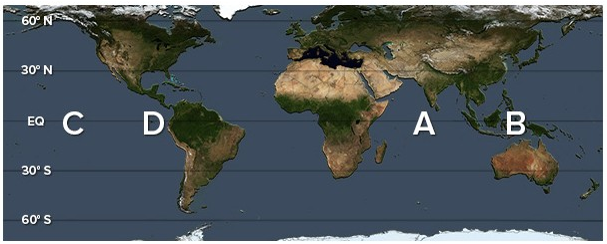
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
What impact does the North American Free Trade Agreement have on relations between countries in North America?
A) NAFTA regulates and enforces protections for workers to ensure that they have safe working environments and fair wages. B) NAFTA eliminates tariffs and trade restrictions, facilitating export and import between countries in North America. C) NAFTA sets up regulations limiting industrial pollution in all three countries, ensuring the costs of manufacturing are similar in each country. D) NAFTA eliminates trade restrictions on products from embargoed countries.
List the eight essential changes in the way people perceive and use their environments necessary to meet sustainable development
A country is currently creating 40 million tons of toxic waste per year. The table below shows the marginal costs and benefits of reducing the amount of toxic waste to various amounts. What number belongs in place of X?
A. 700 B. 900 C. 1300 D. 1500