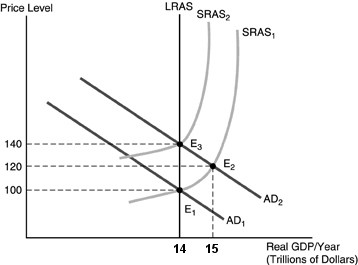
 Using a graph above, show the short-run and long-run effects of an expansionary monetary policy.
Using a graph above, show the short-run and long-run effects of an expansionary monetary policy.
What will be an ideal response?
In the above figure, E1 is the original equilibrium. The increase in the money supply causes the aggregate demand to increase due to the direct and indirect effects. Real GDP increases in the short run to $15 trillion and the price level increases to 120. Once input owners revise their expectations about prices, the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to SRAS2, real GDP returns to $14 trillion, and the price level increases to 140. The long-run effect of the expansionary monetary policy is to increase the price level.
You might also like to view...
When personal computers were first produced, the price was very high. As time passed, the price of personal computers fell because
A) the initial price was too high and nobody bought personal computers. B) people's incomes increased and personal computers are an inferior good. C) the demand for personal computers decreased. D) there were technological advances in the production of personal computers. E) None of the above answers is correct.
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A monopolist has a vertical supply curve because it is a price taker. B) A monopolist's supply curve is the supply curve of the entire market. C) A monopolist does not have a supply curve because its production decision is independent of price. D) A monopolist has a horizontal supply curve because it is the only seller in the market.
A tax on primary resource use would
a. Increase recycling rates and raise the costs of some products b. Increase recycling rates and not affect product costs c. Decrease recycling rates and raise the cost of some products d. Decrease recycling rates and not affect product costs e. Decrease recycling rates but the effect on prices is unknown
As the economy ________, the size of the multiplier will become smaller.
A. slows B. approaches full employment C. experiences stagflation D. goes into a recession