An increase in Swiss interest rates will cause
A) an increase in the demand for U.S. dollars and an increase in the exchange rate of Swiss francs per dollar.
B) a decrease in the demand for U.S. dollars and a decrease in the exchange rate of Swiss francs per dollar.
C) an increase in the supply of U.S. dollars and a decrease in the exchange rate of Swiss francs per dollar.
D) a decrease in the supply of U.S. dollars and an increase in the exchange rate of Swiss francs per dollar.
C
You might also like to view...
An important type of information asymmetry is:
A. adverse selection. B. ethical constraint. C. advantage imbalance. D. information hazard.
The Federal Reserve cannot affect the price level directly; therefore, the Fed typically uses the following as its policy target:
A. Interest rates B. Government expenditures C. Inflation
Exhibit 10-8 Aggregate demand and supply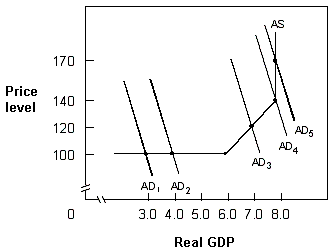
A. real GDP will increase from $3.0 to $7.0, and the price level will remain the same. B. real GDP will increase from $3.0 to $4.0, and the price level will remain the same. C. real GDP and the price level will both remain the same. D. real GDP will increase from $3.0 to $4.0, and the price level will increase from 100 to 140.
A monopolist faces the inverse demand curve P = 60 - Q. It has variable costs of Q2 so that its marginal costs are 2Q, and it has fixed costs of 30. At its profit-maximizing output level, the monopoly's average cost is
A) 11. B) 13. C) 17. D) 21.5.