Two forces act on a 6.00-kg object. One of the forces is 11.0 N. If the object accelerates at 2.00 m/s2, what is the greatest possible magnitude of the other force?
a. 33.0 N
c. 3.0 N
b. 23.0 N
d. 1.0 N
B
You might also like to view...
Discuss the mass, temperature, color and size of an M3V star, compared to the Sun
What will be an ideal response?
All of the following are true. Which of these gives evidence that quasars were more common when the universe was young than they are today?
A) They are more common at very great distances. B) They are very bright. C) They are active galactic nuclei. D) We don't see them in every galaxy.
Coulomb's Law: As shown in the figure, the charge Q is midway between two other charges. If Q = -7.5 nC, what must be the charge q1 so that charge q2 remains stationary as Q and q1 are held in place?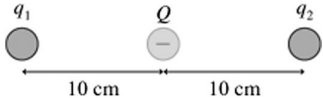
A. 30 nC B. 15 nC C. 7.5 nC D. 60 nC
A mass suspended from a spring moves with the greatest velocity
A. at the end points of its motion B. at the equilibrium position C. midway between the end point of its motion and the equilibrium position