International trade benefits
A) only the exporter.
B) only the importer.
C) both the exporter and the importer.
D) neither the exporter nor the importer.
E) the exporter at all times and sometimes also the importer.
C
You might also like to view...
The optimal collective decision rule _____
a. will be 100 percent if collective decision-making costs are high b. will be simple majority rule if external costs are extremely large c. has declining external costs as voting rule moves from unanimity d. is likely to be less than majority rule
The basic difference between mixed and pure bundling is that
A) in pure bundling, buyers can only buy a collection of goods, while with mixed bundling, they can buy the collection or the components of the collection separately. B) in pure bundling, buyers must buy a collection of goods, while in mixed bundling, buyers pay different prices for the same collection. C) price elasticities are generally elastic when pure bundling is used while unitary elasticity is prevalent when mixed bundling is used. D) the costs of production vary between the two types of bundling.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.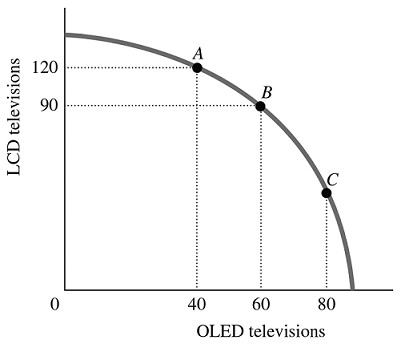 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. For this economy to move from Point C to Point B, ________ additional LCD TVs could be produced when the production of OLED TVs is reduced by 20.
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. For this economy to move from Point C to Point B, ________ additional LCD TVs could be produced when the production of OLED TVs is reduced by 20.
A. exactly 30 B. exactly 60 C. fewer than 30 D. more than 30
The greatest benefit to an economy from international trade is:
A. greater employment in the export sector of the economy. B. the economic power it gives a nation over other countries. C. full employment of its labor force. D. consumption beyond domestic production possibilities.