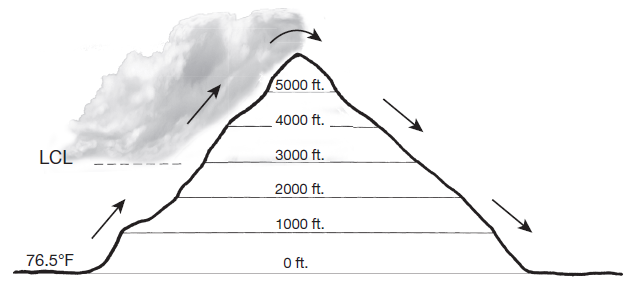
Why is the parcel now warmer than it was at sea level on the windward side (what is the source of the heat energy)?
Assume that a parcel of air is forced to rise up and over a 6000-foot-high mountain (as shown). The initial temperature of the parcel at sea level is 76.5°F, and the lifting condensation level (LCL) of the parcel is 3000 feet. The DAR is 5.5°F>1000 feet and the SAR is 3.3°F>1000 feet. Assume that condensation begins at 100% relative humidity and that no evaporation takes place as the parcel descends. Indicate calculated temperatures to 1 decimal place.
What will be an ideal response?
The release of latent heat during condensation reduced the rate of cooling above the LCL on the windward side.
You might also like to view...
Geocoding is used by Internet browsers such as Google and Yahoo for location-based services.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
How would a droplet formed on a hygroscopic nuclei compare to a droplet that formed on a hydrophobic nuclei?
A) The hygroscopic nuclei droplet would be larger. B) The droplet on the hydrophobic nuclei would be smaller. C) The droplet on the hygroscopic nuclei would form at a lower relative humidity. D) Both A and C E) Both B and C.
________ tides occur at the first quarter moon.
A. Spring B. Mixed C. Semidiurnal D. Neap E. Diurnal
What substance makes up much of the interior layers of Neptune, marked with an arrow?
A) Hydrogen/helium B) Ice C) Rock D) Methane