Macroeconomists think that
a. most questions about individual markets are more important than the overall economy.
b. questions of overall unemployment are less important than the jobs of particular workers.
c. the details of resource allocation and individual market prices are less important than the amount of national output.
d. the causes of unemployment usually lie with the personalities of individual workers.
e. the price of particular products is more important than the overall price level.
c
You might also like to view...
The outcome of the game in the figure shown will be:
This figure shows the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.
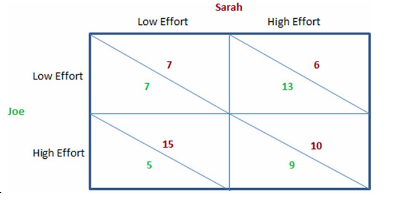
A. Joe puts forth high effort and Sarah puts forth low effort.
B. Joe puts forth low effort and Sarah puts forth high effort.
C. Joe and Sarah both put forth low effort.
D. Joe and Sarah both put forth high effort.
The branch of economics that focuses on outcomes in highly aggregated markets, such as the markets for labor or consumption goods, is called: a. macroeconomics
b. positive economics. c. normative economics. d. microeconomics.
Which of the following is often referred to as the basic postulate of economics?
a. Individuals act only out of selfish motives. b. Incentives matter--individuals respond in predictable ways to changes in personal costs and benefits. c. The accuracy of the assumptions is the best test of an economic theory. d. The value of a good is objective; it is equal to the cost of producing the good.
In Figure 45.3, the fact that workers must pay for their apprenticeship in order to be certified is shown by 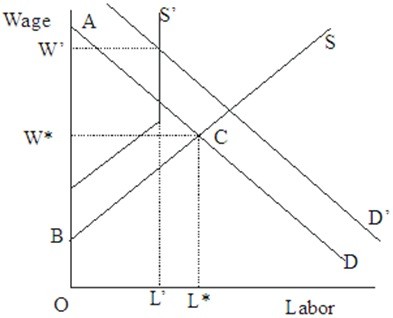 Figure 45.3
Figure 45.3
A. the shift in the old supply curve. B. the increase in the demand curve. C. the slope of the old demand curve. D. the kinked shape of the new supply curve.