Refer to the table below. In moving from combination a to e, the marginal rate of substitution of X for Y:
The table shows an indifference schedule for several combinations of X and Y.
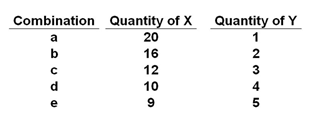
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Stays the same
D. Decreases and then increases
B. Decreases
You might also like to view...
Which of the following does NOT contribute to the marginal productivity of workers?
A) discrimination B) talent C) experience D) education
A utility-maximizing consumer would not consume more of a good if
a. marginal utility increases as more is consumed b. total utility diminishes as more is consumed c. MU/P < 1 d. MU/P < 1 e. MU/P = 1
The equilibrium of aggregate supply and aggregate demand represents the:
A. total of all goods and services produced in the major sectors of the economy. B. general price level of the economy with respect to goods and services households purchase. C. overall state of the national economy. D. All of these are true.
After nearly tripling the money supply after the housing market crash and subsequent financial crisis, inflation:
A. has slowly increased, due to restored consumer confidence in the market, increasing the marginal propensity to consume. B. continued to fall, due to the lack of consumer confidence in the market, decreasing the marginal propensity to consume. C. began to spiral out of control, due to the newfound solvency of banks, increasing lending and thus the money multiplier effect. D. stayed relatively low, due to the lack of lending by banks, reducing the effectiveness of the money multiplier.