A monopolist faces the inverse demand curve P = 60 - Q. It has variable costs of Q2 so that its marginal costs are 2Q, and it has fixed costs of 30. The monopoly's profit-maximizing output is
A) 5.
B) 10.
C) 15.
D) 20.
C
You might also like to view...
When marginal private benefit is equal to marginal private cost,
A. the activity in question generates no negative externality. B. all negative externalities have been internalized. C. all positive externalities have been internalized. D. all of the above E. a or b
Variables A and B are inversely related. If we plot A on the horizontal axis and B on the vertical axis, the line that connects combinations of A and B in a two-variable diagram is
A) parallel to the horizontal axis. B) downward-sloping (left to right). C) parallel to the vertical axis. D) upward-sloping (left to right). E) a or c
These are the cost and revenue curves associated with a monopolistically competitive firm.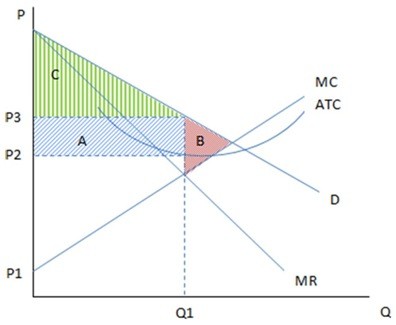 According to the graph shown, the monopolistically competitive firm:
According to the graph shown, the monopolistically competitive firm:
A. will earn negative profits (a loss) equal to area B. B. will earn positive profits equal to area C. C. will earn negative profits (a loss) equal to area A. D. will earn positive profits equal to area A.
The marginal revenue product is
A) the change in total output resulting from a one-unit change in variable output. B) the change in marginal output resulting from a one-unit change in variable input. C) the change in total revenue resulting from a one-unit change in variable input. D) the change in marginal revenue resulting from a one-unit change in variable input.