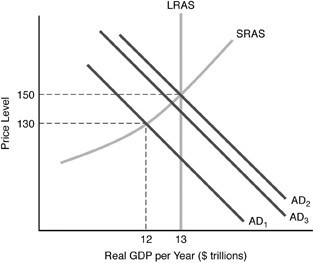
 Refer to the above figure. Suppose that the economy starts at AD1. If the government reduces taxes, then the economy goes to AD2, but then falls back to AD3. This is an example of
Refer to the above figure. Suppose that the economy starts at AD1. If the government reduces taxes, then the economy goes to AD2, but then falls back to AD3. This is an example of
A. partial crowding-out effect.
B. Ricardian equivalence.
C. complete crowding-out effect.
D. laissez-faire.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
All students should go on to college.
A. True B. False C. Uncertain
____________________: Producing right mix of goods
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
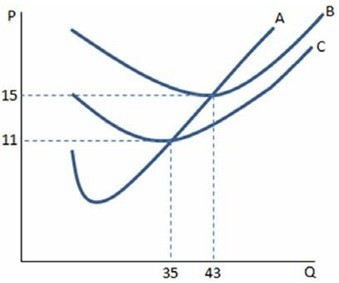 If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and produces at the profit-maximizing level of output, which of the following is true? A firm will:
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and produces at the profit-maximizing level of output, which of the following is true? A firm will:
A. make positive profits any time the price is greater than $15. B. lose money and shut down in the short run if price falls below $15. C. lose money, but continue to operate in the short run if price is at least $15. D. All of these are true.
In the inverted-U theory of R&D:
A. process innovation and product innovation are inversely related. B. technological change is inversely related to scientific discovery. C. R&D expenditures rise continuously as a percentage of firms' sales as industry concentration rises. D. R&D expenditures first rise as a percentage of firms' sales as industry concentration increases, but then fall as higher industry concentration occurs.