A monopolistic competitor is like a monopolist in the short run in that when economic profits are
A) equal to zero, price equals marginal cost.
B) equal to zero, price below marginal cost.
C) greater than zero, changes in output are due to changes to plants by existing firms and there is no entry.
D) greater than zero, price exceeds marginal cost.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Use the figure below to answer the following question.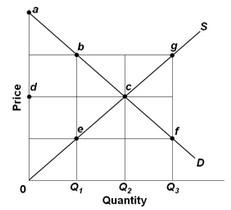 If the output level is Q2, then there will be
If the output level is Q2, then there will be
A. minimum net producer surplus. B. greater marginal benefits than marginal costs of the product. C. productive efficiency. D. maximum deadweight losses.
Explain how BOP disequilibrium is restored under
(a) flexible exchange rates. (b) fixed exchange rates, after you define what a BOP disequilibrium means.
A monopolist's demand curve is given by:
p = 100 + A1/2 – Q where Q is the quantity of output and A is the quantity of advertising. Suppose the cost of advertising and output is given by: C(Q,A) = 10Q + A Determine the profit maximizing quantity of output and advertising.
When we examine the U.S. money supply, the smallest component of M1 is
A) currency and coins. B) transaction deposits. C) certificates of deposit. D) traveler's checks.