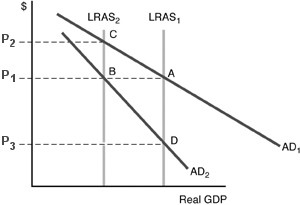
 Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy's initial equilibrium is represented by the intersection of LRAS2 and AD2. Now there is an increase in labor productivity which increases total planned production at any given price level and aggregate demand remains stable. The resulting change in the economy's long-run equilibrium position would be represented by a
Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy's initial equilibrium is represented by the intersection of LRAS2 and AD2. Now there is an increase in labor productivity which increases total planned production at any given price level and aggregate demand remains stable. The resulting change in the economy's long-run equilibrium position would be represented by a
A. movement from C to D.
B. movement from C to B.
C. movement from B to D.
D. movement from A to B.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In the above figure, if the minimum wage is set at $6 per hour, the level of unemployment is ________ hours per week is
A) 40 million B) 30 million C) 20 million D) 0
Which of the following statements about the real loanable funds market is not true?
a. Movements in the real risk-free interest rate cause significant changes in borrowers' willingness and ability to tap the domestic credit market if the demand is highly elastic. b. The more inelastic a nation's supply of real loanable funds, the less sensitive domestic savers, banks, foreigners, and governments are to changes in the real risk-free interest rate. c. Monetary policy is usually stronger in nations with inelastic real loanable funds demands. d. Fiscal policy is usually weaker in nations with elastic real loanable funds demands. e. All of the above are true.
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
A. A firm's total economic cost is at least as large as the firm's total accounting cost. B. A firm's total economic cost includes both explicit cost and implicit cost of the firm. C. A firm's implicit cost is the opportunity cost of non-purchased inputs. D. A firm's total accounting cost is at least as large as the firm's implicit cost.
(Consider This) The U.S. recession that occurred in 2008 and 2009 represented a case where:
A. government policy intervention effectively offset the negative demand shock and minimized the effects on output and employment. B. prices were somewhat flexible, so the impact of the demand shock was felt about the same in terms of price and output changes. C. prices were relatively flexible, minimizing the impact on total output and employment. D. prices were relatively sticky and most of the impact was on total output.