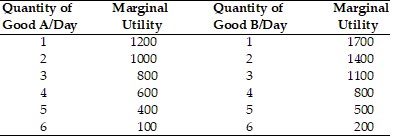
 Refer to the above table. If the price of Good A is $2, the price of Good B is $2, and the consumer has $14, the rational consumer will purchase
Refer to the above table. If the price of Good A is $2, the price of Good B is $2, and the consumer has $14, the rational consumer will purchase
A. 6 units of Good A and 6 units of Good B.
B. 6 units of Good A and 0 units of Good B.
C. 3 units of Good A and 4 units of Good B.
D. 3 units of Good A and 3 units of Good B.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Until the United States Civil War, The Unites States had a
A) gold-based monetary standard. B) silver-based monetary standard. C) bimetallic monetary standard consisting of silver and gold. D) bimetallic monetary standard consisting of copper and silver. E) bimetallic monetary standard consisting of copper and gold.
Those that believe that the recent period of slow growth will pass and that higher levels of growth can be created through liberal policies focus on ones that would cause
A. decreases in aggregate supply. B. increases to aggregate supply. C. increases to aggregate demand. D. increases in interest rates.
The theory of efficiency wages explains why
a. setting wages at the equilibrium level may increase unemployment. b. it may be in the best interest of firms to offer wages that are above the equilibrium level. c. the most efficient way to pay workers is to pay them according to their skills. d. it is efficient for firms to set wages at the equilibrium level.
Why might asymmetric information contribute to the problem of a market failure?
What will be an ideal response?