Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.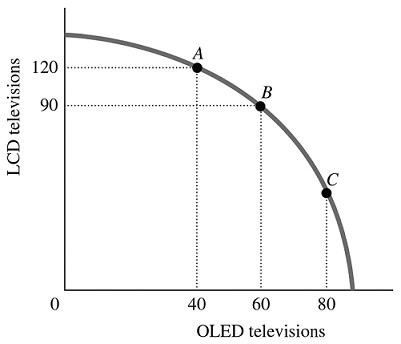 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
A. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 60 additional OLED televisions.
B. 90 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions.
C. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions.
D. 120 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED televisions.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following explain(s) better the fact that computers are cheaper now than 10 years ago?
a. c and d. b. c and e. c. The technology used in the production of computers has improved during this period. d. Resources used in the production of computers have become cheaper during this period. e. The demand for computers has increased substantially during this period.
Consider a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. At its current output of 200 units, marginal revenue is $28 . At this output, average total cost is minimized and equals $25 . Given this information, what should the firm do?
a. Continue to produce 200 units, since costs per unit are minimized b. Increase output beyond 200 units, since this higher output will yield the profit maximizing output level. c. Decrease output below 200 units, since this lower output will result in the profit maximizing output level. d. More information is needed to determine the firm's next step.
Suppose that the U.S. undertakes a policy to increase its saving rate. This policy will likely
a. have no impact on the growth rate of real GDP per person. b. decrease the growth of real GDP per person for a few years. c. increase the growth of real GDP per person for several decades. d. permanently increase the growth rate of real GDP per person.
The marginal cost curve:
A. rises when the point of diminishing marginal productivity is reached. B. declines until average total cost increases. C. first rises and then declines. D. rises when the average total cost curve lies above the average variable cost curve.