A perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue
A) is greater than its price.
B) is less than price because a firm must lower its price to sell more.
C) is equal to its price.
D) may be either greater or less than its price, depending on the quantity sold.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The marginal rate of substitution is the
a. quantity of a good a consumer receives for $1 payment b. income a consumer gives up to acquire one unit of the good c. ratio of the prices of two goods d. rate at which the consumer is willing to trade one good for another good e. relative quantity of a good that two consumers trade
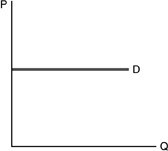 Refer to the above figure. Demand is
Refer to the above figure. Demand is
A. perfectly elastic. B. unitary elastic. C. perfectly inelastic. D. undetermined without more information.
Which of the following would cause the equilibrium price of apple juice to decrease and the equilibrium quantity of apple juice to increase?
A) a decrease in the price of apples B) an increase in the price of apples C) an increase in the price of orange juice, a substitute for apple juice D) a decrease in the price of granola bars, a complement for apple juice
Public goods represent a market failure because
A. there is incomplete information regarding their quality. B. they are provided by firms with market power. C. by their very nature they are nonexcludable and nonrival, which makes it difficult for the private sector to supply them profitably. D. positive externalities are created through their production.