Refer to the diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total cost:
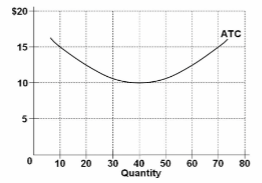
A. is $10.
B. is $40.
C. is $400.
D. cannot be determined from the information provided.
C. is $400.
You might also like to view...
Lisa views pizzas and burritos as goods. If she prefers a bundle of 4 burritos and 4 pizzas to a bundle of 4 burritos and 5 pizzas, which property of consumer preference is violated?
What change in the assumptions could lead a rational consumer to prefer the first bundle?
Suppose the price of a product is less than its average variable cost. When the firm's fixed obligations are completely ended, it will now most likely:
a. make an economic profit. b. go out of business. c. expand to a bigger operation. d. continue to be shut down. e. break even.
If a natural disaster were to cause a negative long-run supply shock to the economy, once the economy adjusts, the new equilibrium will be at a:
A. higher price level and lower level of output. B. lower price level and lower level of output. C. higher price level and higher level of output. D. lower price level and higher level of output.
An accounting identity is
A) when the balance of payments is running a surplus or deficits. B) when the balance of trade is in surplus or deficit. C) an expression of values that are equivalent by definition. D) special drawing rights.