The basic goals of total utility maximization, total profit maximization, and total welfare maximization explain most market activity.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
True
The goal of consumers is to maximize total utility, the business firm's goal is to maximize total profit, and the government's goal is total welfare maximization.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is FALSE about saving?
A) Saving adds to wealth. B) Income left after paying taxes can either be consumed or saved. C) Saving equals wealth minus consumption expenditures. D) Saving is the source of funds used to finance investment.
Table B shows the pricing options for two medical doctors operating as an oligopoly in a rural market. Which of the following pricing strategies does Table 8 depict?
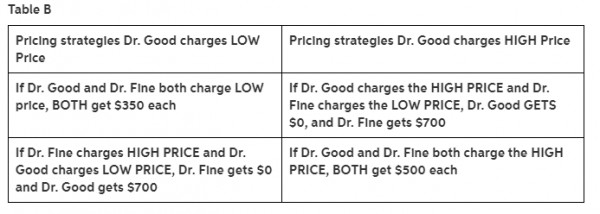
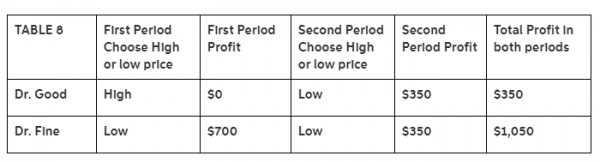
a) Dr. Fine always plays “Tit-for-Tat” and Dr. Good always plays “Tit-for-Tat.”
b) Dr. Fine always plays “Tit-for-Tat” and Dr. Good always chooses the “Low” price.
c) Dr. Good always plays “Tit-for-Tat” and Dr. Fine always chooses the “Low” price.
d) Dr. Good always chooses the “Low” price and Dr. Fine always chooses the “Low” price.
e) When there is only a single period in which to choose and Dr. Fine does not know what Dr. Good will do, Dr. Fine always chooses the Nash Noncooperative Equilibrium price strategy.
What effect do import restrictions have on prices?
a. They cause prices to rise. b. They cause prices to drop. c. They often cause prices to rise steeply and then drop. d. They usually do not have any lasting effect on price.
If a developing country has sufficient reserves, the buying and selling of foreign currency by the central bank is:
A. likely to have a much smaller impact on the exchange rate than in developed countries. B. completely ineffective on the exchange rate. C. likely to have a much greater impact on the exchange rate than in developed countries. D. likely to have roughly the same impact on the exchange rate as in developed countries.