When maximizing profit, the perfect competitor ______ produces at the output at which MC = MR; the monopolist ____ produces at the output at which MC = MR.
A. always; always
B. sometimes; sometimes
C. always; sometimes
D. sometimes; always
A. always; always
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 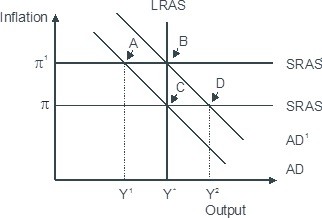
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
In the economic way of thinking, the costs of a recession are predominantly
A) the costs of using money. B) the excessive costs of advertising in the face of persistent, falling demand. C) the costs of disappointed expectations and discoordination of plans. D) the costs associated with high nominal interest rates.
According to the Keynesians, labor contracts
a. are unimportant for modern labor markets because few worker are unionized. b. mean that real wages are inflexible. c. mean that money wages never adjust. d. imply that nominal wages adjust, but only periodically.
Diversification of a portfolio
a. can eliminate market risk, but it cannot eliminate firm-specific risk. b. can eliminate firm-specific risk, but it cannot eliminate market risk. c. increases the portfolio's standard deviation. d. is not necessary for a person who is risk averse.