Refer to Table 2-15. What is George's opportunity cost of cultivating a garden?
A) one-half of a garden cultivated B) two lawns mowed
C) two-thirds of a garden cultivated D) one and a half lawns mowed
B
You might also like to view...
With downward-sloping monetary policy and IS curves,the aggregate demand curve is
A) downward sloping. B) flat. C) vertical. D) upward sloping.
Carla spends all her income on two goods: apples and bananas. The price of an apple is $2 and the price of a banana is $1 . If Carla's marginal utility of an apple is 4 and her marginal utility of a banana is 3, she should consume
a. more apples and fewer bananas to maximize total utility b. more bananas and fewer apples to maximize total utility c. more apples and more bananas to maximize total utility d. fewer apples and fewer bananas to maximize total utility e. exactly what she is consuming because she always makes the most rational choice each time she spends a dollar.
Other things equal, a price discriminating monopolist will:
A. realize a smaller economic profit than a nondiscriminating monopolist.
B. produce a larger output than a nondiscriminating monopolist.
C. produce the same output as a nondiscriminating monopolist.
D. produce a smaller output than a nondiscriminating monopolist.
Refer to the accompanying figure. If the market for doughnuts is perfectly competitive, then assuming this firm can earn enough revenue to cover its variable cost, it should produce: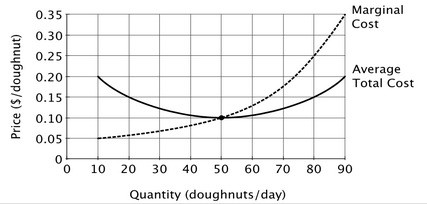
A. the quantity of doughnuts at which average total cost is minimized. B. the quantity of doughnuts at which marginal cost equals the market price. C. 50 doughnuts per day. D. the quantity of doughnuts at which average total cost equals the market price.