Suppose the two countries can trade shares in the ownership of their perspective assets. Further assume that a Home owner of a 25 percent share in Foreign land
He will receive 25 percent share in Foreign land and thus receives 25 percent of the annual Foreign kiwi fruit harvest. Further assume that also that a Foreign owner of a 25 percent share in Home land is permitted. In this case, a Foreigner is entitled to 25 percent of the Home harvest. Calculate the expected value of kiwi fruit for each investor.
Good year at Home: 75 + 12.5 = 87.5 tons with probability 0.5
Bad year at Home: 37.5 from Home and 25 from Foreign = 62.5 with probability 0.5.
The expected return is: 0.5 ? 87.5 + 0.5 ? 62.5 = 75.
You might also like to view...
Since the mid-1980s, Federal Reserve policies have often been described as attempting
A) accelerated takeoffs. B) sustained growth. C) stalling tactics. D) soft landings.
Developing countries do:
A. compete with one another for foreign investment, and this competition reduces the benefits from foreign investment. B. not compete with one another for foreign investment, because they have sufficient domestic saving to finance their investment needs. C. not compete with one another for foreign investment, because they lack the infrastructure to attract it in the first place. D. compete with one another for foreign investment, but this competition is beneficial to developing countries because it insures a more efficient allocation of resources.
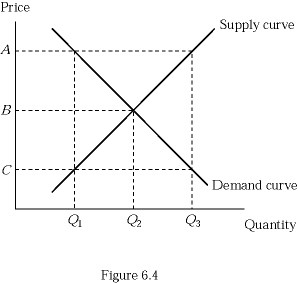 Refer to Figure 6.4. Suppose that the market is currently in equilibrium and the government decides to impose a maximum price equal to price A in the graph. How will the equilibrium quantity and price change as a result of the price ceiling?
Refer to Figure 6.4. Suppose that the market is currently in equilibrium and the government decides to impose a maximum price equal to price A in the graph. How will the equilibrium quantity and price change as a result of the price ceiling?
A. It won't. The price ceiling is above the equilibrium, so the market stays at equilibrium. B. It will cause a shortage because at the price ceiling, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. C. It will cause a surplus because at the price ceiling, the quantity demanded is below the quantity supplied. D. It won't. The price ceiling is below the equilibrium, so the market stays at equilibrium.
The equilibrium wage rate in an industry is found by
A) the intersection of the market demand curve for labor and the marginal revenue product curve of labor. B) the intersection of the firm's demand curve for labor and the firm's supply curve of labor. C) the intersection of the market demand curve for labor and the market supply curve of labor. D) negotiations between the union leadership and the managers of the firms.