Use a one-dimensional array to solve the following problem: A company pays its salespeople on a commission basis. The salespeople receive $200 per week, plus 9% of their gross sales for that week. For example, a salesperson who grosses $5000 in sales in a week receives $200 plus 9% of $5000, a total of $650. Write an application (using an array of counters) that determines how many of the salespeople earned salaries in each of the following ranges (assuming that each salesperson’s salary is truncated to an integer amount): $200–299, $300–399, $400–499, $500–599, $600–699, $700–799, $800– 899, $900–999 and over $999. Allow the user to enter the sales for each employee in a JTextField. The user should click the Calculate JButton to calculate that salesperson’s sala
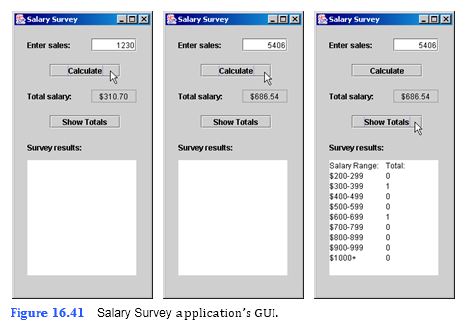
a) Copying the template to your working directory. Copy the C:Examples Tutorial16ExercisesSalarySurvey directory to your C:SimplyJava directory.
b) Opening the template file. Open the SalarySurvey.java file in your text editor.
c) Create an array that represents the number of salaries in each range. On lines 32–33, create an empty int array called resultArray to store the number of employees who earn salaries in each range. Use line 32 for a comment and line 33 to create the array. The elements of resultArray will represent different ranges in the survey. Specify the size of resultArray as 11 using keyword new. There are 9 salary ranges in this application. For convenience, we use a slightly larger array, of size 11. You will ignore the first two elements of this array. The elements you will use are at locations
2–10, where each location represents a salary range (location 2 represents the range
200–299, location 3 represents the range 300–399, etc.). The proper locat
```
1 // SalarySurvey.java
2 // Application that takes information about employee salaries and
3 // uses an array to keep track of the number of employees in each
4 // salary range.
5 import java.awt.*;
6 import javax.swing.*;
7 import java.awt.event.*;
8 import java.text.DecimalFormat;
9
10 public class SalarySurvey extends JFrame
11 {
12 // JLabel and JTextField for entering total sales
13 private JLabel enterSalesJLabel;
14 private JTextField enterSalesJTextField;
15
16 // JButton to calculate the total salary
17 private JButton calculateJButton;
18
19 // JLabel and JTextField for displaying the total salary
20 private JLabel salaryJLabel;
21 private JTextField salaryJTextField;
22
23 // JButton for displaying the totals
24 private JButton totalsJButton;
25
26 // JLabel and JTextArea for displaying the survey results
27 private JLabel resultJLabel;
28 private JTextArea resultJTextArea;
29
30 DecimalFormat dollars = new DecimalFormat( "$0.00" );
31
32 // set up result array
33 int[] resultArray = new int[ 11 ];
34
35 // no-argument constructor
36 public SalarySurvey()
37 {
38 createUserInterface();
39 }
40
41 // create and position GUI components; register event handlers
42 private void createUserInterface()
43 {
44 // get content pane for attaching GUI components
45 Container contentPane = getContentPane();
46
47 // enable explicit positioning of GUI components
48 contentPane.setLayout( null );
49
50 // set up enterSalesJLabel
51 enterSalesJLabel = new JLabel();
52 enterSalesJLabel.setBounds( 20, 20, 80, 20 );
53 enterSalesJLabel.setText( "Enter sales:" );
54 contentPane.add( enterSalesJLabel );
55
56 // set up salesJTextField
57 enterSalesJTextField = new JTextField();
58 enterSalesJTextField.setBounds( 120, 20, 70, 20 );
59 enterSalesJTextField.setHorizontalAlignment(
60 JTextField.RIGHT );
61 contentPane.add( enterSalesJTextField );
62
63 // set up calculateJButton
64 calculateJButton = new JButton();
65 calculateJButton.setBounds( 55, 60, 110, 20 );
66 calculateJButton.setText( "Calculate" );
67 contentPane.add( calculateJButton );
68 calculateJButton.addActionListener(
69
70 new ActionListener() // anonymous inner class
71 {
72 // event handler called when calculateJButton is pressed
73 public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent event )
74 {
75 calculateJButtonActionPerformed( event );
76 }
77
78 } // end anonymous inner class
79
80 ); // end call to addActionListener
81
82 // set up salaryJLabel
83 salaryJLabel = new JLabel();
84 salaryJLabel.setBounds( 20, 100, 80, 20 );
85 salaryJLabel.setText( "Total salary:" );
86 contentPane.add( salaryJLabel );
87
88 // set up salaryJTextField
89 salaryJTextField = new JTextField();
90 salaryJTextField.setBounds( 120, 100, 70, 20 );
91 salaryJTextField.setHorizontalAlignment( JTextField.CENTER );
92 salaryJTextField.setEditable( false );
93 contentPane.add( salaryJTextField );
94
95 // set up totalsJButton
96 totalsJButton = new JButton();
97 totalsJButton.setBounds( 55, 140, 110, 20 );
98 totalsJButton.setText( "Show Totals" );
99 contentPane.add( totalsJButton );
100 totalsJButton.addActionListener(
101
102 new ActionListener() // anonymous inner class
103 {
104 // event handler called when totalsJButton is pressed
105 public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent event )
106 {
107 totalsJButtonActionPerformed( event );
108 }
109
110 } // end anonymous inner class
111
112 ); // end call to addActionListener
113
114 // set up resultJLabel
115 resultJLabel = new JLabel();
116 resultJLabel.setBounds( 20, 180, 100, 20 );
117 resultJLabel.setText( "Survey results:" );
118 contentPane.add( resultJLabel );
119
120 // set up resultJTextArea
121 resultJTextArea = new JTextArea();
122 resultJTextArea.setBounds( 20, 210, 170, 180 );
123 contentPane.add( resultJTextArea );
124
125 // set properties of application's window
126 setTitle( "Salary Survey" ); // set title bar string
127 setSize( 220, 450 ); // set window size
128 setVisible( true ); // display window
129
130 } // end method createUserInterface
131
132 // calculate salary; increment counters
133 private void calculateJButtonActionPerformed( ActionEvent event )
134 {
135 int sales = Integer.parseInt( enterSalesJTextField.getText() );
136 double salary = 200 + .09 * sales;
137 int index = ( int ) salary / 100;
138
139 if ( index >= 10 )
140 {
141 resultArray[ 10 ]++;
142 }
143 else
144 {
145 resultArray[ index ]++;
146 }
147
148 salaryJTextField.setText( dollars.format( salary ) );
149
150 } // end method calculateJButtonActionPerformed
151
152 // display salary ranges and totals
153 private void totalsJButtonActionPerformed( ActionEvent event )
154 {
155 int lowerBound;
156 int upperBound;
157
158 resultJTextArea.setText( "Salary Range:\tTotal:\n" );
159
160 for ( int i = 2; i <= 9; i++ )
161 {
162 lowerBound = i * 100;
163 upperBound = lowerBound + 99;
164
165 resultJTextArea.append( "$" + lowerBound + "-" +
166 UpperBound + '\t' + resultArray[ i ] + "\n" );
167 }
168
169 resultJTextArea.append( "$1000+\t" + resultArray[ 10 ] );
170 resultJTextArea.append( "$1000+\t" + resultArray[ 10 ] );
171 } // end method totalsJButtonActionPerformed
172
173 // main method
174 public static void main( String[] args )
175 {
176 SalarySurvey application = new SalarySurvey();
177 application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
178
179 } // end method main
180
181 } // end class SalarySurvey
```
You might also like to view...
Facts about people, events, things, or ideas are called:
A) information. B) specifics. C) statistics. D) data.
The option to add a section to a presentation is on the ________ tab
A) View B) Insert C) Home D) Review
What are the areas that should be documented in a forensic investigation? What, in your opinion, makes documentation the most important aspect of forensic science?
What will be an ideal response?
?Which protocol specifies rules for transferring files from one computer to another?
A. ?Internet Protocol B. ?File Transfer Protocol C. ?Transmission Control Protocol D. ?Computer Transfer Protocol