A wealthy executive is holding money, waiting for a good time to invest in the stock market. This action would be an example of the
A. asset demand for money.
B. use of money as a medium of exchange.
C. transactions demand for money.
D. creation of fiat money.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If your nominal income in 2014 was $50,000, and prices doubled between 2014 and 2017, to have the same real income, your nominal income in 2017 must be
A) $50,000. B) $75,000. C) $90,000. D) $100,000.
If reserves in the banking system increase by $200, then checkable deposits will increase by $500 in the simple model of deposit creation when the required reserve ratio is
A) 0.04. B) 0.25. C) 0.40. D) 0.50.
The product approach to calculating GDP
A) adds together the market values of final goods and services produced by domestic and foreign-owned factors of production within the nation in some time period. B) includes the market value of goods and services produced by households for their own consumption but excludes the value of the underground economy. C) is superior to the income approach because, unlike the income approach, it gives us the real value of output. D) adds together the market values of final goods, intermediate goods, and goods added to inventories.
If Daniel has budget constraint C in the graph shown, what would cause it to shift to budget constraint B?
This graph shows three different budget constraints: A, B, and C.
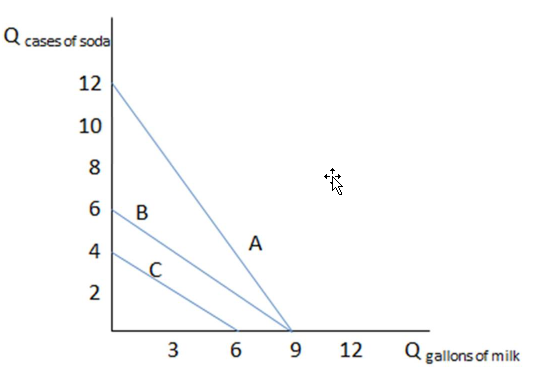
A. An increase in the price of milk
B. A decrease in the price of soda
C. An increase in the price of soda
D. None of these changes alone could cause a shift from C to B.