Which of the following policies are likely to increase national savings?
a. running larger government budget deficits.
b. decreasing taxes on stock dividends.
c. reducing taxes on consumption.
d. having to pay higher interest rates on the national debt.
e. none of the above.
B
You might also like to view...
Suppose a single firm has constant marginal cost and faced the demand curve 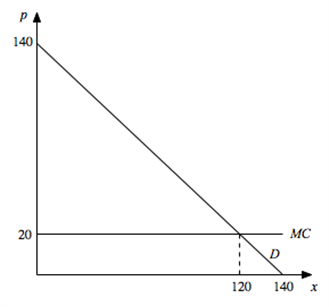
b. Assuming no recurring fixed costs, how much profit does the monopolist make? How much consumer surplus is generated? c. If the monopolist were able to first-degree price discriminate instead, how much would he produce? How much profit would he make? How much consumer surplus is generated? d. Which outcome is more efficient and why? What will be an ideal response?
If the price elasticity of demand for U.S. automobiles is higher in Europe than it is in the United States, and transport costs are zero, a price-discriminating monopolist would charge
A) the same price for autos in the United States as in Europe. B) a lower price for autos in the United States than in Europe. C) a higher price for autos in the United States than in Europe. D) a less profitable price for autos in the United States than in Europe.
The multiplier effect refers to the fact that a change in spending (aggregate demand) will
What will be an ideal response?
A reduction in a country's rate of inflation should
A. increase its exports. B. lead to a negative trade balance. C. increase its imports. D. lead to an outflow of SDRs.